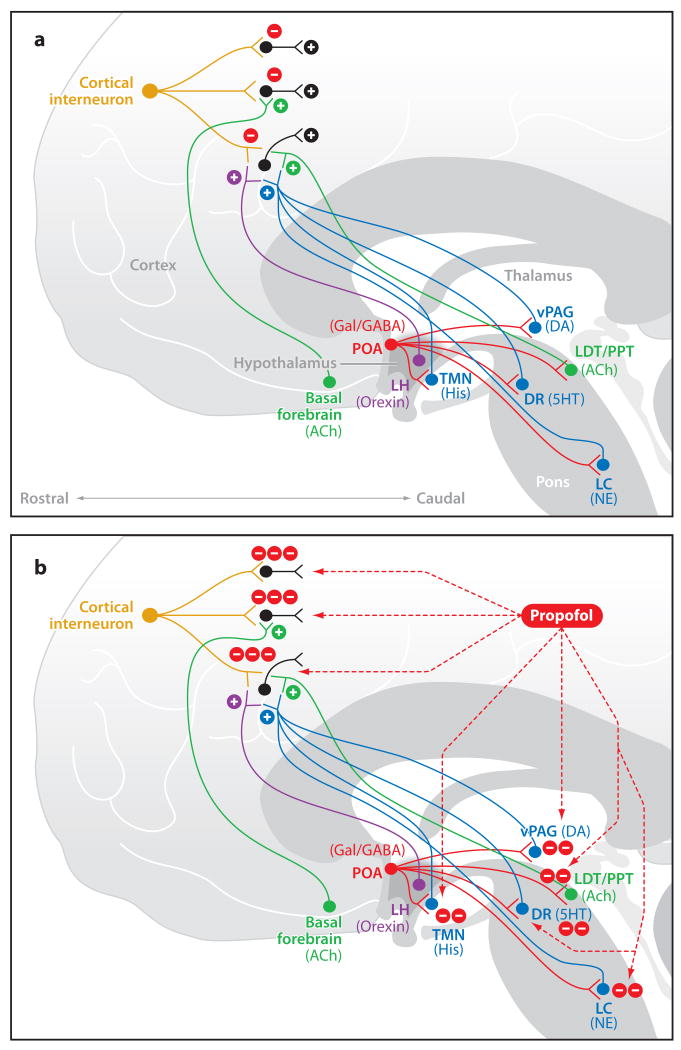
Figure 1.
GABAergic signaling during the awake state (a) and during propofol administration (b). (a) A cortical interneuron during wakefulness mediating control of pyramidal neurons and being modulated by ascending arousal centers. Also shown are inhibitory projections from the POA to the arousal-promoting nuclei. (b) Propofol enhances GABAergic transmission in the cortex and at the inhibitory projections from the POA to the arousal centers. Abbreviations: 5HT, serotonin; ACh, acetylcholine; DA, dopamine; DR, dorsal raphe; GABA, gamma aminobutyric acid; Gal, galanin; His, histamine; LC, locus coeruleus; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental area; LH, lateral hypothalamus; NE, norepinephrine; POA, preoptic area; PPT, pedunculopontine tegmental area; TMN, tuberomamillary nucleus; vPAG, ventral periaquaductal gray.