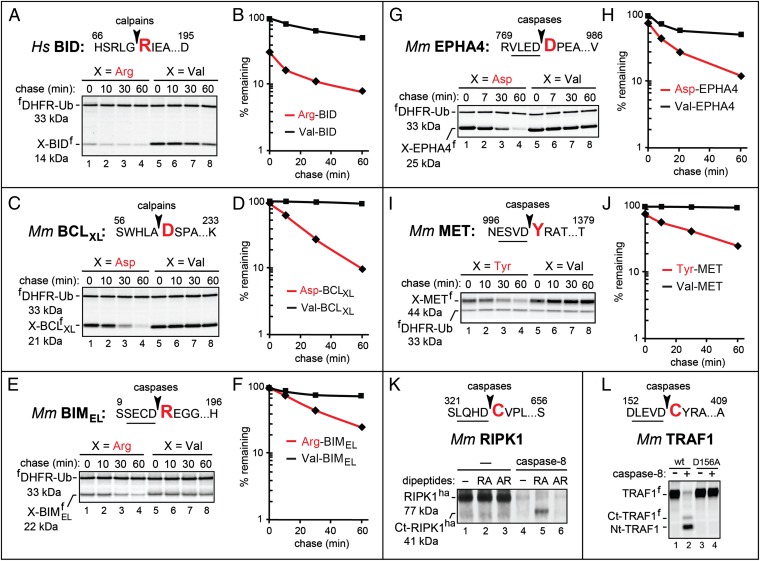
Fig. 3.
Arg-BID, Asp-BCLXL, Arg-BIMEL, Asp-EPHA4, and Tyr-MET as short-lived N-end rule substrates. (A) Human Arg71-BIDf (produced from fDHFR-UbR48-Arg71-BIDf), the otherwise identical Val71-BIDf, and the calpain cleavage site in BID. Fig. 2 shows notations and pulse-chase procedures. (B) Quantification of A. (C) Same as in A but with mouse X61-BCLXLf (X = Asp, Val). (D) Quantification of C. (E) Same as in A but with mouse X14-BIMELf (X = Arg, Val). (F) Quantification of E. (G) Same as in A but with mouse X774-EPHA4f (X = Asp, Val). (H) Quantification of G. (I) Same as in A but with mouse X1001-METf (X = Tyr, Val). (J) Quantification of I. (K) Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8. Mouse RIPK1ha was expressed in reticulocyte extract for 45 min at 30 °C, followed by the addition of cycloheximide and either recombinant human caspase-8 or buffer alone. The samples were incubated for 30 min followed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-ha antibody. Lane 1, RIPK1ha; lanes 2 and 3, same as lane 1 but with the Arg-Ala and Ala-Arg, respectively, at 5 mM added the start of assays; lanes 4–6, same as lanes 1–3, respectively, but with caspase-8 as well. Note the caspase-generated C-terminal RIPK1 fragment migrating at the Mr of the 41-kDa Cys326-RIPK1ha in lane 5 (with 5 mM Arg-Ala) but not in lane 4 (no added dipeptide) or lane 6 (with 5 mM Ala-Arg). (L) Cleavage of TRAF1 by caspase-8. Mouse TRAF1f and its caspase-resistant mutant TRAF1D156A(f) were expressed in reticulocyte extract for 1 h at 30 °C in the presence of [35S]methionine, followed by the addition of cycloheximide, unlabeled methionine and cysteine, and either caspase-8 or buffer alone. Samples were incubated for another 30 min, followed by SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. Lanes 1 and 3, TRAF1f and TRAF1D156A(f), respectively; lanes 2 and 4, same as lanes 1 and 3, respectively, but with caspase-8. Note the much lower (degradation-mediated) level of the 35S-labeled, caspase-generated C-terminal TRAF1 fragment denoted as Ct-TRAF1f (it migrates at the expected Mr of the Cys157-TRAF1 fragment) compared with the N-terminal fragment (denoted as Nt-TRAF1f), despite the higher content of 35S-Met in Ct-TRAF1f.