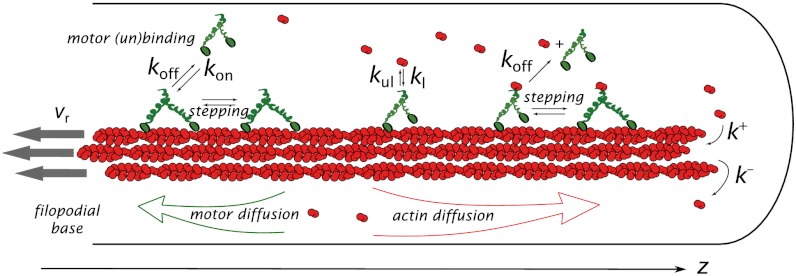
Fig. 1.
A representation of the filopodial model is shown with kinetics scheme of chemical reactions. A filopodium is a cylindrical tube with a bundle of parallel actin filaments inside enveloped by cell’s membrane. The motors can walk on filaments (with speed v determined by forward and backward stepping rates) or diffuse in the solution (with diffusion constant of 5 μm2/s). They can bind and unbind to the filaments (with rates kon and koff) and, when on filaments, load, and unload G actin (with rates kl and kul). A loaded motor can detach from the filament simultaneously releasing G actin. Thus, there is no G actin bound to motors in the solution, fulfilling the nonsequestrating regime condition.