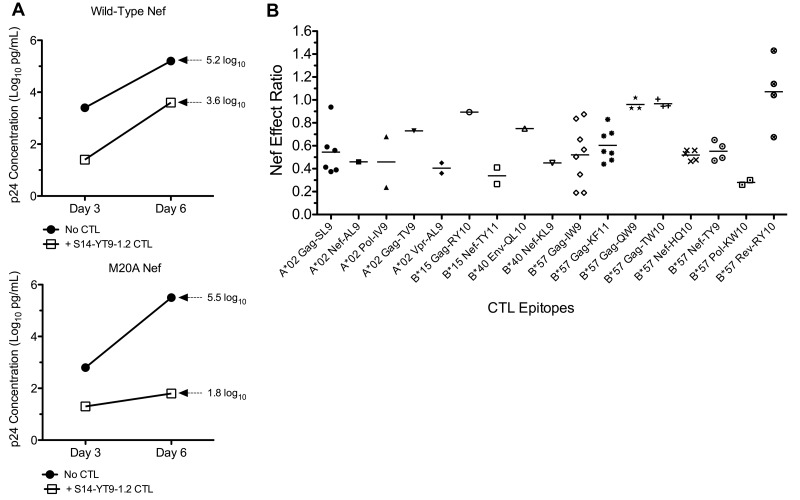
Figure 1.
Impact of Nef on the antiviral activity of HIV-1–specific CTLs. The susceptibility of HIV-1–specific CTLs to Nef-mediated HLA-I down-regulation was measured using a previously described viral suppression assay. (A) CTL clone S14-YT9-1.2 (B*57 restricted and Nef specific) was tested for inhibition of NL4-3.1 virus containing wild-type Nef or Nef-M20A (unable to down-regulate HLA-I) in parallel. Replication was assessed by measuring supernatant Gag p24 antigen (log10 pg/mL) and plotted over time. Inhibition of wild-type virus at day 6 was 1.6 log10 units (5.2-3.6 = 1.6) and inhibition efficiency was 0.3 (1.6/5.2 = 0.31). Inhibition of M20A-Nef virus at day 6 was 3.7 log10 units (5.5-1.8 = 3.7) and inhibition efficiency was 0.7 (3.7/5.5 = 0.67). Therefore, the Nef-effect ratio was 0.42 (0.31/0.67 = 0.46). A ratio of 0 would therefore indicate complete evasion mediated by Nef and a ratio of 1 would indicate no effect of Nef. (B) The Nef effect on viral inhibition is plotted for a panel of HIV-1–specific CTL clones. Each data point represents the average Nef-effect ratio of a CTL clone across multiple independent experiments; the horizontal bar represents the mean.