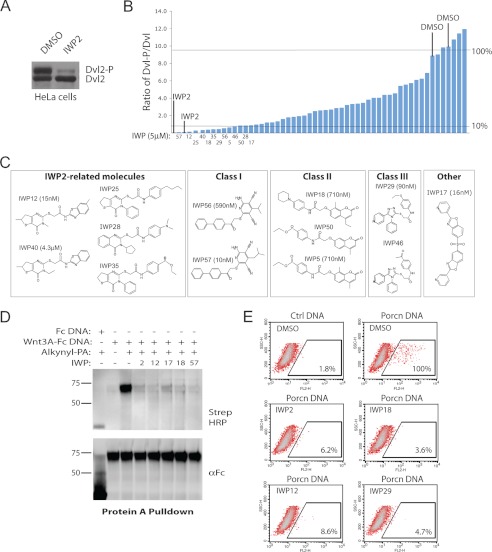
FIGURE 4.
Diverse chemical scaffolds support Porcn inhibition by targeting the putative active site. A, Dvl2 phosphorylation status in HeLa cells reflects Porcn activity. IWP2 inhibits Dvl2 phosphorylation in HeLa cells indicating cell-autonomous Wnt-mediated signaling in these cells as previously described. B, identification of additional Porcn inhibitors. The IWP compound collection of Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitors was tested for their ability to inhibit Dvl2 phosphorylation in HeLa cells. The ratio of phosphorylated to unphosphorylated Dvl protein in cells treated with each IWP compound was determined by densitometric analysis of Western blot results as shown in A. Compounds inhibiting 90% or more of Dvl phosphorylation are labeled. C, shared chemical scaffolds yielding the most active IWP molecules. Compounds are clustered based on their similarity to IWP2 or shared chemical structures. IC50 against Wnt/β-catenin pathway response as measured by STF is provided for at least one representative compound from each class. D, novel IWP compounds disrupt Wnt protein acylation. Wnt3A-Fc protein from cells treated with alkynyl-PA in the presence of indicated IWP compound or DMSO was subjected to an alkyne cycloaddition reaction to label fatty acylated Wnt3A with biotin. Biotinylated protein separated on SDS-PAGE was visualized with streptavidin HRP. E, novel Porcn inhibitors likely bind directly to Porcn. The ability of indicated IWP compounds to compete for IWP-Cy3 binding to Porcn was determined as before.