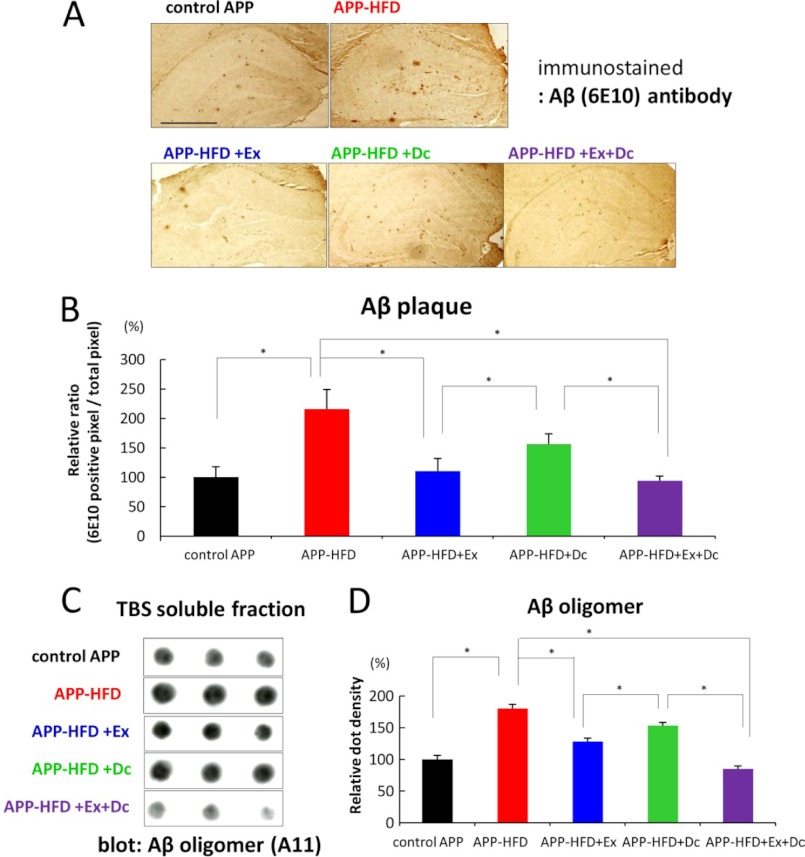
FIGURE 4.
Exercise ameliorated HFD-induced Aβ accumulation when compared with diet control. A, immunohistochemical analysis using anti-Aβ (6E10) antibody. Representative images of Aβ-immunostained hippocampus sections from control APP, APP-HFD, APP-HFD+Ex, APP-HFD+Dc, and APP-HFD+Ex+Dc induced mice, respectively, are shown. Scale bar, 2 mm. B, cerebral Aβ loads determined by immunohistochemical and morphometric analyses. The cerebral Aβ deposition was significantly decreased in APP-HFD+Ex mice when compared with that in APP-HFD+Dc mice (F(4, 15) = 18.35, *, p = 0. 039). C, the amount of Aβ oligomers in the TBS-soluble fractions of control-APP, APP-HFD, APP-HFD+Ex, APP-HFD+Dc, and APP-HFD+Ex+Dc mice analyzed by filter trap assay using anti-Aβ oligomer (A11) antibody. As described in Ref. 12, the Aβ monomer and low weight oligomers passed through the membrane pore (200-nm pore size), and high weight oligomers were detected in this assay. D, statistical analysis of dot density. The average band density of the control APP samples was regarded as 100%, and that of other groups was relatively indicated. The relative density of APP-HFD+Ex mice was significantly decreased when compared with that of APP-HFD+Dc mice (F(4, 10) = 47.42, *, p = 0.011).