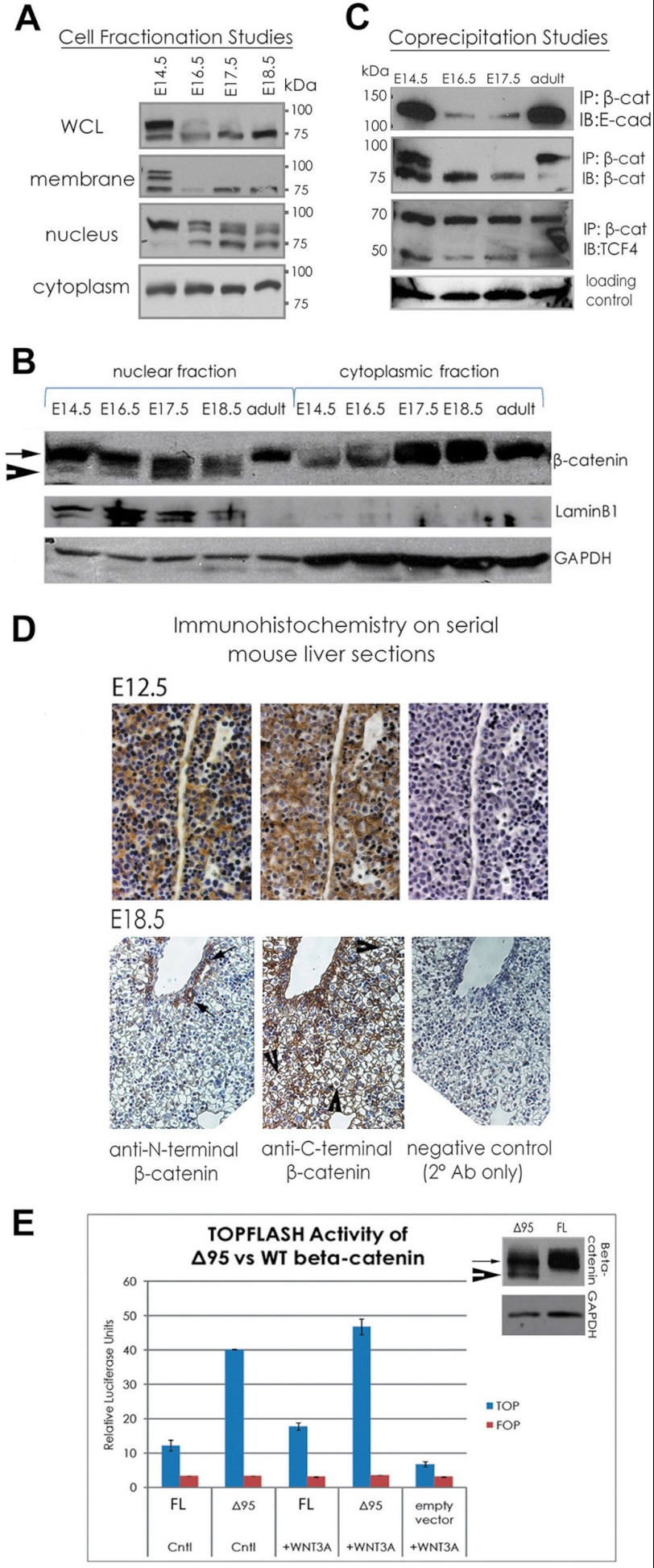
FIGURE 2.
Truncated β-catenin is expressed in differentiating hepatocytes and is transcriptionally active (A and C). Cell fractionation studies reveal truncated β-catenin present in membrane and nuclear fractions of liver during E16.5, E17.5, and E18.5, whereas cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions contained full-length β-catenin (B). Co-immunoprecipitation indicates that truncated β-catenin binds both E-cadherin and TCF4. IgG band served as loading control (D). Immunohistochemistry with antibodies against N terminus of β-catenin to detect full-length β-catenin and C terminus to detect both forms of β-catenin reveal that truncated β-catenin (regions positive with anti-C-terminal but not anti-N-terminal antibody) is located in the nuclei and at membranes of hepatocytes. Full-length β-catenin expression is limited to biliary epithelial cells only. E, Δ95 β-catenin transfection of HEK293 cells activates TOPFLASH, supporting a role as a nuclear transactivator (full-length (FL) β-catenin versus Δ95 β-catenin; control (Cntl) medium p < 0.0003; WNT3A medium p < 0.003, Student's t test). The immunoblot (right) on transfected cells shows expression levels of Δ95 and full-length β-catenin in each. IP, immunoprecipitate; WB, Western blot; WCL, whole cell lysates.