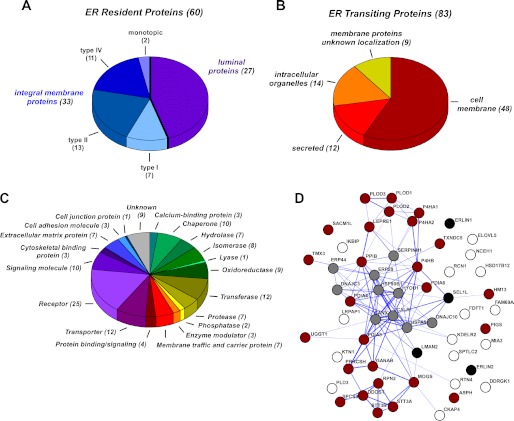
FIGURE 1.
Overview of the ER acetyl-lysine proteome analysis. A and B, topological classification of acetylated resident (A) and transiting (B) proteins. The complete list of proteins and peptides is in supplemental Tables S1 and S2. C, functional classification of all acetylated proteins (resident and transiting). Proteins were assigned based on the Protein Analysis THrough Evolutionary Relationships (PANTHER) classification system. D, interaction network from STRING analysis of acetylated resident proteins. STRING analysis was performed using “experiments, database, and text mining evidences” as prediction methods (using STRING 9.0). Description of the current STRING database as well as analysis procedures can be found in Ref. 11. Thickness of the connecting lines indicates the confidence score of the association (thicker lines indicate stronger confidence). Resident proteins were grouped based on functions as follows: gray, chaperones; red, proteins involved with post-translational modification; black, proteins involved with quality control and ER-associated protein degradation; white, other.