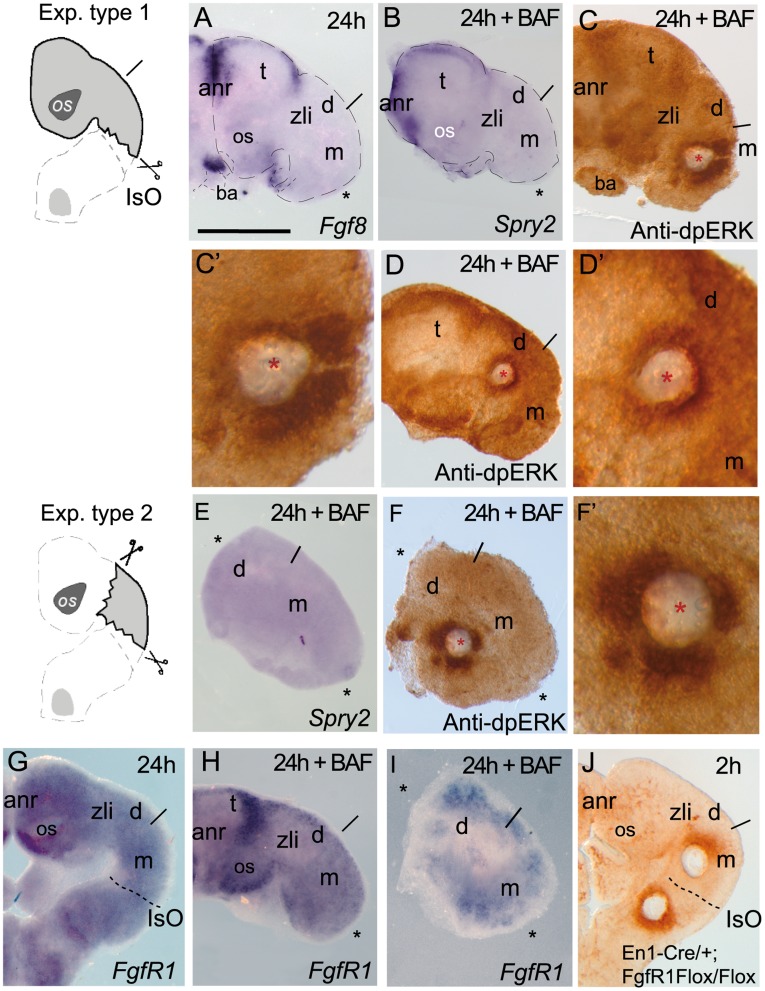
Figure 5. The position of FGF8- related secondary organizers determines the polarity of ERK1/2 activation.
.A-D’) show the type 1 experimental manipulation in ONTCs where a dissection of the IsO region was made, left for 24 hours in vitro and thereafter it was incubated with BAF for 2h after an implantation of a FGF8b bead in mesencephalon (C-C’) or middle diencephalon (D-D’). Fgf8 mRNA (A) and Sprouty 2 (B) were maintained at anterior neural ridge (ANR), optic stalk (os) and branquial arches (ba) but they were absent in caudal regions of the ablated ONTCs. Bead implantations in mesencephalon modified ERK1/2 polarization towards caudal parts of the bead (C, C’; for comparison see Figure 4C). Bead implantations in the diencephalon maintained symmetric distribution of ERK1/2 activity around the bead (D,D’). In these experiments FgfR1 expression (G) was maintained in IsO ablations (H). E,F,F” and I show type 2 experimental manipulation assays in ONTCs where rostral forebrain (anr included) and hindbrain (type 1 experiment) were ablated. Under these conditions and following the BAF incubation protocol, the tissue left did not express any FGF8 downstream genes (Sprouty2; D) and the ectopic induction of ERK1/2 activity was found symmetrically distributed around the bead (F and F’) on FgfR1 positive domain (I). In fact the lack of FgfR1 in the midbrain and hindbrain region, does not disturb ERK1/2 polarizing effects on both brain regions (J). Scale bars are 0,5 mm except for C’, E’ that are 100 µm.