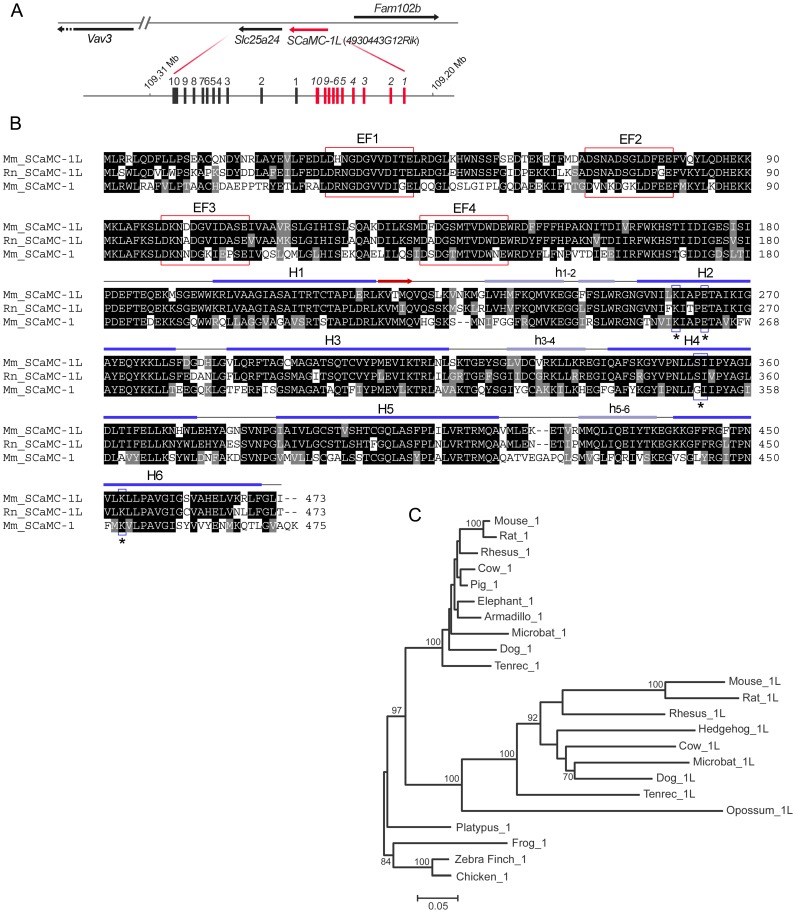
Figure 1. SCaMC-1Like, SCaMC-1L, a new SCaMC paralog emerged by a tandem duplication in mammals.
(A) Scheme of the head-to-tail tandem array of mouse SCaMC-1 (slc25a24) and 4930443G12Rik/SCaMC-1L genes. SCaMC-1, SCaMC-1L and flanking loci are represented by arrows indicating transcription orientation. SCaMC-1/SCaMC-1L intron-exon organization is also shown. Exons are indicated by filled boxes (not to scale) and numbered. (B) Alignment of predicted mouse and rat SCaMC-1L protein sequences (Mm_SCaMC-1L and Rn_SCaMC-1L) with that of mouse SCaMC-1 (slc25a24, Mm_SCaMC-1). Alignment was performed with ClustalW and colored with BOXSHADE 3.21 software. Predicted EF-hand calcium-binding motifs are indicated by red boxes. Secondary structure prediction for the region homologous to mitochondrial carriers, amino acids 181 to end, of Mm_SCaMC-1L was obtained using Jpred3 server [69]. The predicted transmembrane helices are indicated (H1–H6), matrix loops are marked in lower case letter and the β-strand region by an arrow. The residues proposed as participants in substrate interactions in H2, H4 and H6 [34] are included in boxes and marked with asterisks. (C) Phylogenetic relationships among SCaMC-1 and SCaMC-1L paralogs. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using amino acid sequences derived from exons 2 to 7 with the neighbor-joining method (MEGA 4.0, [70]) and PAM distances. Non-mammalian vertebrate SCaMCs were used as outgroups. The scale of branch lengths is indicated (number of substitutions per site). Percentage bootstrap values are shown in each node (500 replicates, only bootstrap values of 60% or more are shown). The accession numbers of annotated SCaMC-1 and SCaMC-1L proteins as well as the amino-acid sequences of manually assembled orthologs are compiled in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2. See alignment in Figure S6.