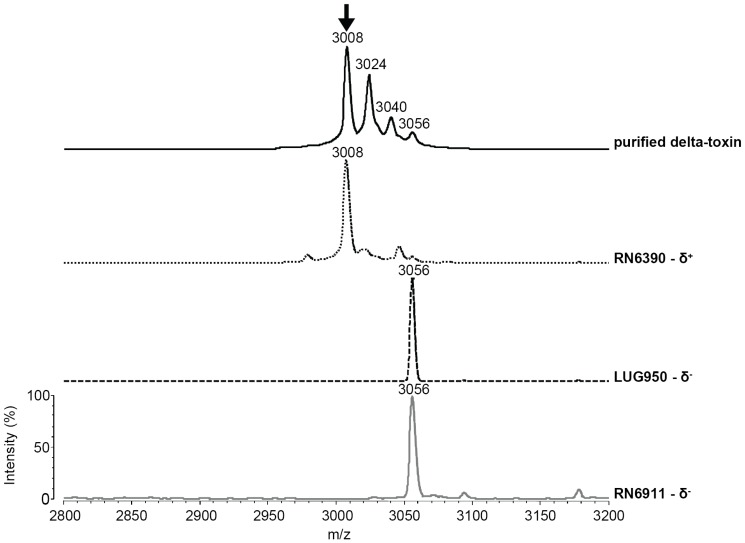
Figure 1. Identification of the delta-toxin peak using purified delta-toxin and isogenic strains.
Purified delta-toxin from wild-type Staphylococcus aureus (500 ng) or strains mutated in the accessory gene regulator (agr) locus were spotted on the target and analysed in the Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization – Time-of-Flight mass spectrometer with a mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) range of 2800 to 3200 Thomson (Th). Setting were as follows: mass range 2000–20000 Th; laser power 80 Volts; pulse extraction 8330 Th; number of laser fires per sample 500; noise cut off 10 mVolts with a minimum resolution of 300; Auto quality mode activated. The settings of the detector were according to the linear mode with a positive source of 20000 Th and a negative pulsed extraction at 2100 Th. The arrow in panel A indicates delta-toxin; additional peaks of 3024, 3040 and 3056 Th correspond to contaminants resulting from the purification of the toxin from S. aureus culture supernatant. Isogenic strains were: RN6390 (delta positive strain) RN6911 (full agr knock-out, delta negative strain) and LUG 950 (rnaIII knock-out, delta negative strain).