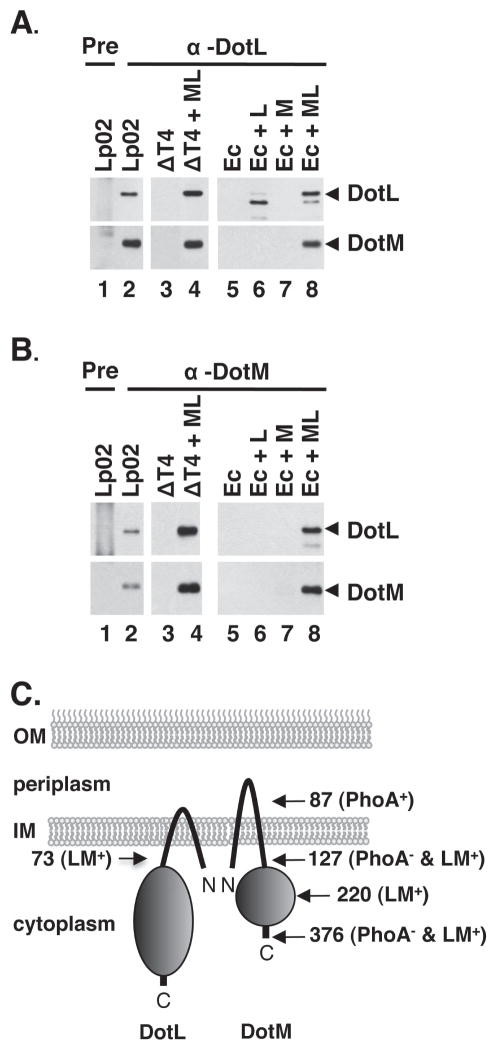
Figure 2. Interactions between DotL, DotM, IcmS and IcmW demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation.
(A) DotM co-immunoprecipitates with DotL. Immunoprecipitations using L. pneumophila or E. coli lysates (genotypes shown at top) were performed using pre-immune serum (“pre”) or DotL-specific antiserum followed by Western blotting using antibodies specific to DotL or DotM, as indicated to the right of each blot (arrowheads designate full-length protein). Lysates were made from the following strains: lanes 1 and 2 are wild-type Legionella (Lp02), lane 3 is Δdot/icm + vector (JV4191), lane 4 is Δdot/icm + dotML (JV4192), lane 5 is E. coli + vector (JB3188), lane 6 is E. coli + dotL (JB3189), lane 7 is E. coli + dotM (JB3190), and lane 8 is E. coli + dotML (JB3191).
(B) DotL co-immunoprecipitates with DotM. Same as in (A) except DotM-specific antiserum was used (lanes 2–8).
(C) Schematic representation of the orientation of and interaction between DotL and DotM in the inner membrane. Sites of PhoA and two-hybrid fusions are indicated by arrows and the final amino acid in each fusion. PhoA positive and negative fusions are shown by a plus or a minus sign. Fusions that were positive in the two-hybrid assay are indicated by an LM+ designation.