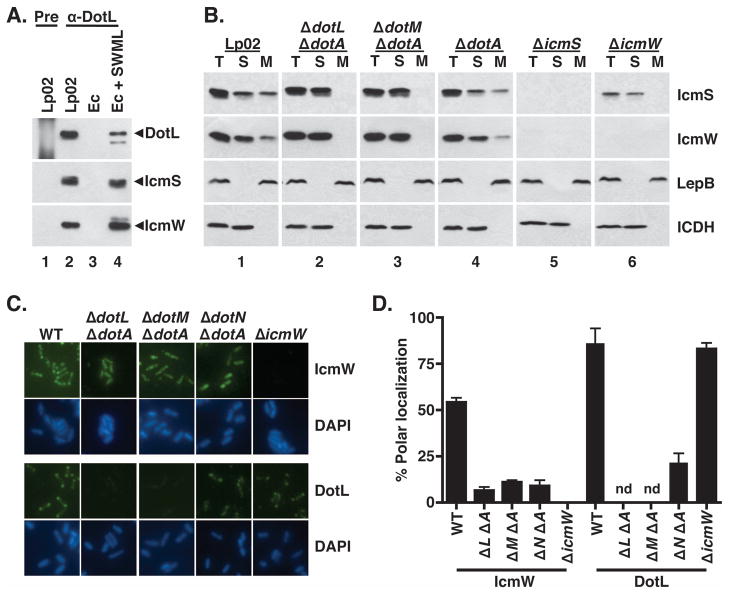
Figure 3. IcmS and IcmW are cytoplasmic proteins that associate with the bacterial membrane at the poles in a DotL/DotM/DotN-dependent manner.
(A) IcmS and IcmW co-immunoprecipitate with DotL. Immunoprecipitations were performed using pre-immune serum (“pre”, lane 1) or DotL-specific antiserum (lanes 2–4) and samples were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to DotL, IcmS, and IcmW. Lysates were made from the following strains: lanes 1 and 2 are wild-type (Lp02), lane 3 is E. coli + vector (JB3188), and lane 4 is E. coli + icmS + icmW + dotML (JB4728).
(B) L. pneumophila strains were grown to exponential phase, fractionated, followed by Western blotting with antibodies specific to IcmS, IcmW, DotL, the inner membrane control protein LepB, and the cytoplasmic control protein ICDH (indicated on the right). Fractions are labeled as follows: (T) total cellular protein, (S) soluble proteins, and (M) membrane proteins. Panel 1 is wild type (Lp02), panel 2 is ΔdotL ΔdotA (JV2422), panel 3 is ΔdotM ΔdotA (JV5361), panel 4 is ΔdotA (JV2064), panel 5 is ΔicmS (JV1962), and panel 6 is ΔicmW (JV3598).
(C and D) Polar localization of DotL and IcmW are dependent on the subcomplex. L. pneumophila strains were grown to exponential phase, and immunofluorescence microscopy analysis was conducted as described. Affinity purified DotL and IcmW antibodies were used to probe wild type (Lp02), ΔdotL ΔdotA, ΔdotM ΔdotA, ΔdotN ΔdotA, and ΔicmW strains. DNA was stained with DAPI. Polar staining of DotL and IcmW was quantified from three independent experiments with one hundred cells scored in each experiment. Polar localization of DotL was not determined (nd) for the ΔdotL and ΔdotM strains due to the absence of detectable antigen. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean.