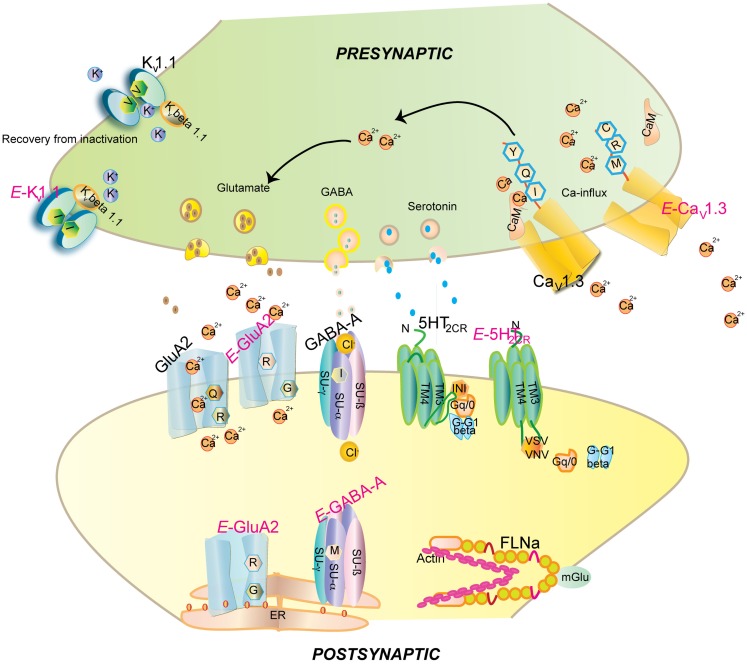
Figure 1.
Impact of editing on selected neuronal receptors and proteins. Shown are several receptors and channels in their unedited (black) and edited (E, in pink) versions. Editing at the Q/R site of ionotropic glutamate receptor GluA2 subunit decreases Ca2+permeability and endoplasmic reticulum exit efficiency. Membrane trafficking of the GABAA receptor is reduced by editing of I to M in the alpha3 subunit. Editing of the serotonin 5-HT2c receptor converts the amino acids I-N-I to V-S-V or V-N-V. This reduces G-protein coupling in the receptor. The editing-induced I to V exchange in Kv1.1 (I/V) alters the interaction with Kv β1.1 (see Figure 3 for detail). Editing of the IQ motiv in Cav1.3 to MR abolishes calmodulin binding. Filamin alpha (FLNa) is edited in a region that is known to interact with metabotropic glutamate receptor mGlu7b and some of its relatives.