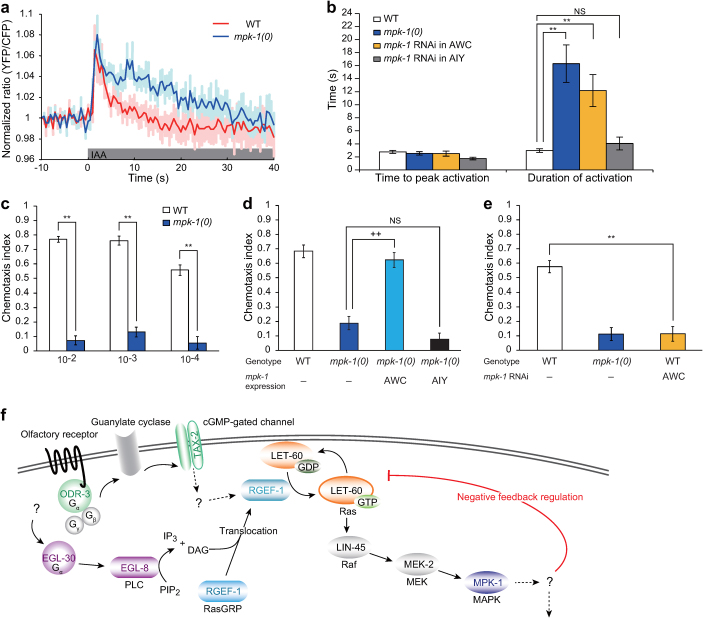
Figure 3. Negative feedback loop controls quick inactivation of Ras.
(a) Ras activity in the AWC neurons in response to 5 × 10−4 dilution of IAA in wild type (WT) (n = 10) and mpk-1(ga117null) mutants (n = 9). The shaded region around the plotted data represents SEM. (b) Average time to peak of Ras activation and average duration of Ras activation in wild type (n = 10), the mpk-1 mutants (n = 9) and wild type with knockdown of mpk-1 functions in AWC (n = 9) or AIY (n = 10). The period between stimulation and peak Ras activation was defined as the ‘time to peak activation’ whereas the period between the peak and a return to the basal ratio value (mean ratio during 10 sec preceding the first application of IAA) was defined as the ‘duration of activation’. Error bars indicate SEM and the asterisks indicate significant differences compared with wild-type samples (**P < 0.01; Dunnett’s test). (c) Chemotaxis to isoamyl alcohol (IAA) in wild type and mpk-1(ga117) mutants (n ≥ 6 assays). IAA dilutions are indicated below the graph. (d) Chemotaxis to 10−3 dilution of IAA of the mpk-1 mutants expressing mpk-1 cDNA in AWC sensory neurons by the odr-1 promoter or AIY interneurons by the AIY-specific ttx-3 promoter (n ≥ 4 assays). (e) Chemotaxis to 10−4 dilution of IAA of wild type with knockdown of mpk-1 functions in AWC (n ≥ 5 assays). Error bars indicate SEM and significant differences are indicated by ** (P < 0.01; Student's t test) and ++ (P < 0.01; Dunnett's test). NS; not significant (P > 0.05). (f) A model of the regulation of the Ras activity in the AWC sensory neurons. Previous reports revealed that EGL-8 (PLCβ) generates diacylglycerol (DAG) and the DAG signal transports RGEF-1 (RasGRP) to membrane regions. Quick activation of Ras via RGEF-1 is mediated by the signal from olfactory sensory signaling and the DAG signal. After activation, Ras is quickly inactivated by negative feedback mechanisms downstream of MPK-1 (MAPK).