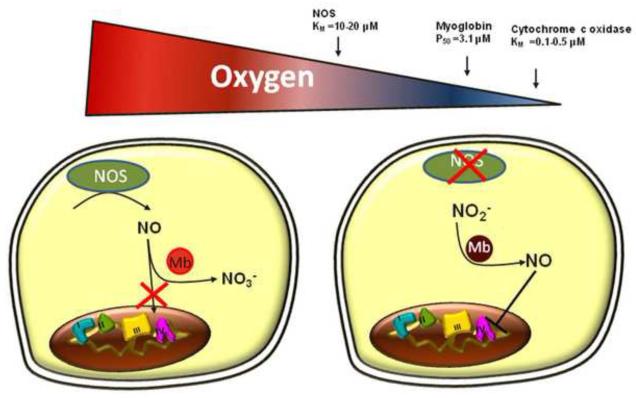
Figure 2. Myoglobin is a normoxic NO dioxygenase and hypoxic nitrite reductase.
In normoxia, NOS enzymatically generates NO which is inactivated by oxygenated myoglobin, preventing respiratory inhibition (left side). As oxygen levels begin to decrease, and endogenous sources of NO are inhibited (nitric oxide synthase KM for oxygen ~10-20μM), myoglobin becomes deoxygenated (P50= 3.1 μM) and shifts to nitrite reduction to generate NO and inhibit respiration, thereby conserving existing oxygen.