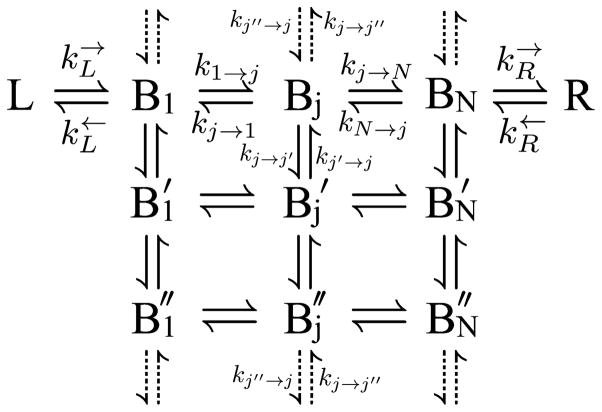
Fig. 2.
The two dimensional rate mechanism consisting of a left electrode (L), a set of bridge sites {Bj}, a right electrode (R), and the transitions between them {k}. We define a “row” as all the bridge sites with the same identifying tick mark, and the total number of “rows” as Nrow. A “column” is all the sites with the same number subscript, and the total number of “columns” is Ncol. Cylindrical boundary conditions are satisfied when the vertical transitions described by the dotted arrows are included. The dotted transitions connect the last row of bridge sites with the first row. The mechanism can be generalized to more sites coupled in from the left electrode {L} and coupled out to the right electrode {R}.