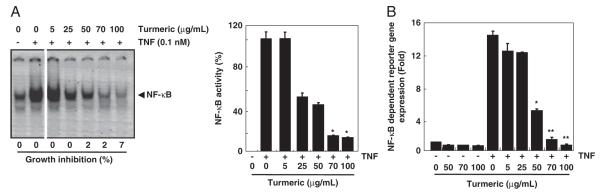
Figure 2.
Effect of turmeric on NF-κB activation. (A) Turmeric suppresses TNF-induced NF-κB activation in a dose-dependent manner. KBM-5 cells (1.5×106 cells/mL) were pre-incubated with turmeric (0, 5, 25, 50, 70, and 100 μg/mL) for 12 h and then treated with 0.1 nM TNF for 30 min. Nuclear extracts were prepared and assayed for NF-κB activation by EMSA (left panel). Values below the EMSA gel indicate percent growth inhibition. Percent inhibition of NF-κB by turmeric was calculated by quantitation of NF-κB bands using a Storm 820 phosphorimager equipped with ImageQuant software (Amersham) (right panel). Data represent the mean±SD of three measurements. *p<0.05, versus control. (B) Suppression of TNF-induced NF-κB-dependent reporter gene expression by turmeric. A293 cells stably transfected with an NF-κB-reporter plasmid were treated with turmeric (0, 5, 25, 50, 70, and 100 μg/mL) for 4 h and then with 1 nM TNF for 24 h. The cell supernatant was then used for SEAP assay. Determinations were made in triplicate. Data represent the mean±SD of three measurements *p<0.05; **p<0.01, significant with respect to control.