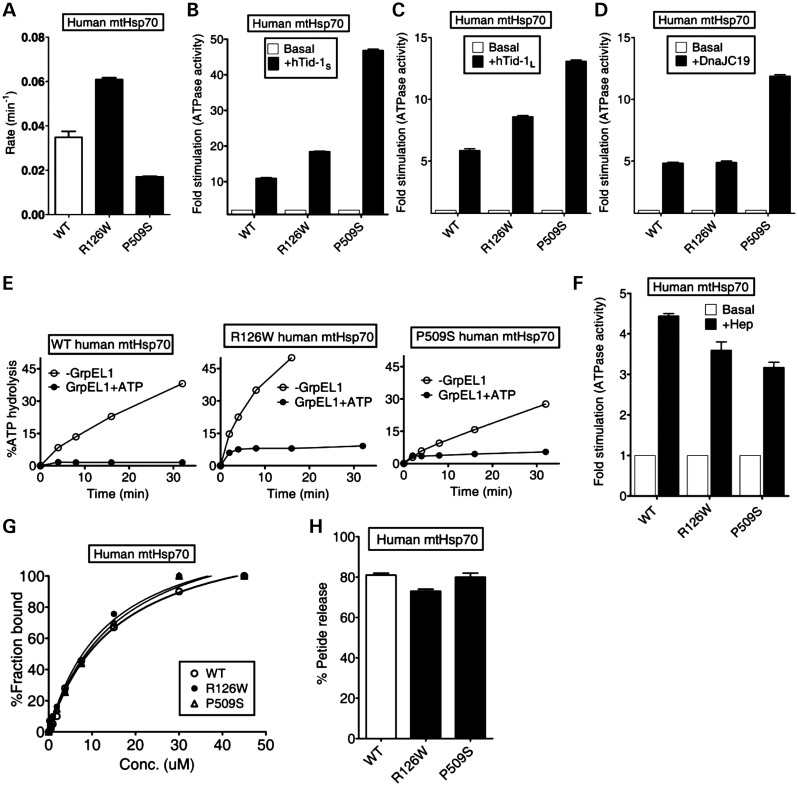
Figure 1.
Biochemical properties of PD variants of human mtHsp70. (A–F) Effects of cochaperones on the ATPase activity. The preformed radiolabeled human mtHsp70-ATP complexes (1 µm) of wild-type (WT) and PD variants (R126W and P509S) were incubated with (A) buffer alone (P < 0.05), (B) 2 µm hTid-1S (P < 0.01), (C) 2 µm hTid-1L (P < 0.05), (D) 2 µm DnaJC19 (P < 0.01), (E) 1 µm GrpEL1, either alone (open circles) or in the presence of 250 µm ATP (closed circles) and (F) 4 µm Hep. ATP hydrolysis was monitored under single turn over conditions at different time intervals and the percentage of ATP-to-Pi conversion was determined. The rate of hydrolysis was calculated using GraphPad Prism 5. Fold stimulation was calculated by setting the basal rate to 1. All error bars are representative of standard deviation obtained from three independent experiments. (G) Substrate interaction studies. 25 nm fluorescein-labeled P5 peptide (F-P5) was incubated with increasing concentrations of the purified proteins and allowed to reach equilibrium. The observed anisotropy values were fitted to a one-site binding equation using the GraphPad Prism 5 software to obtain the Kd values. (H) ATP-induced peptide release. 1000-fold excess ATP was added to saturated protein-F-P5 complexes in the ADP-bound state. The resultant maximal decrease in fluorescence anisotropy of the bound F-P5 was noted to determine the percentage of bound F-P5 released due to ATP binding.