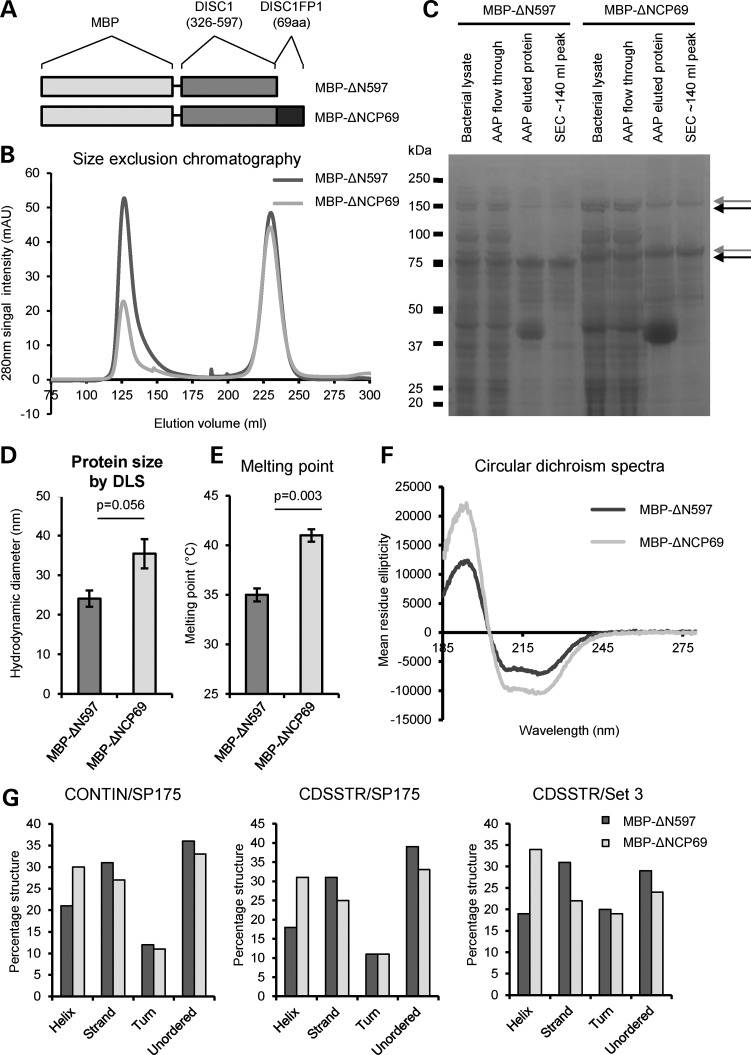
Figure 3.
Biophysical characterization of CP69. (A) Schematic of the recombinant proteins MBP-ΔN597 and MBP-ΔNCP69, drawn to scale. (B) Following amylose affinity purification, size exclusion chromatography separates the recombinant protein (∼140 ml peak) from co-purifying contaminants (later peaks); CV: 320 ml. (C) SDS–PAGE purification gel of MBP-ΔN597 and MBP-ΔNCP69 proteins. AAP, amylose affinity purification; SEC, size exclusion chromatography. Arrows indicate monomers and dimers. (D) Mean hydrodynamic diameters of three independent protein preparations for each of MBP-ΔN597 and MBP-ΔNCP69 determined by DLS. (E) Mean melting temperatures of three independent protein preparations for each of MBP-ΔN597 and MBP-ΔNCP69 determined by DLS at increasing temperatures. (F) CD spectra of MBP-ΔN597 (0.12 mg/ml) and MBP-ΔNCP69 (0.11 mg/ml) in the far-UV range is shown, with mean residue ellipticity and wavelength (measured from 280 to 185 nm) plotted along the y-axis and x-axis, respectively. (G) Deconvolution of the CD spectra using different algorithms and data sets.