Figure 2. Hypomorphic XBP1 in the intestinal epithelium results in a pro-inflammatory milieu and increased susceptibility to microbial challenges.
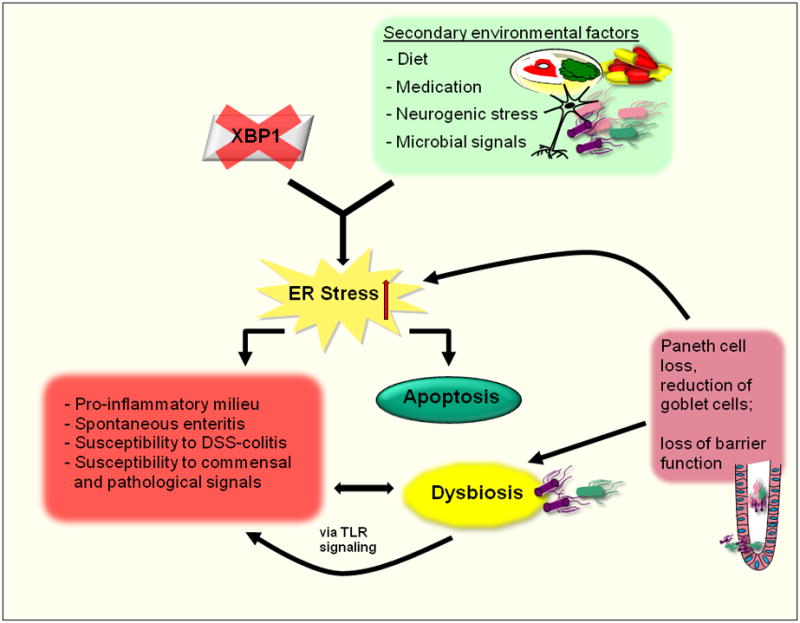
Rare variants of the XBP1 gene result in loss of XBP1 function. In combination with secondary environmental factors, such as diet, medication, neurogenic stress or microbial signals, this generates unabated ER stress, a pro-inflammatory milieu, spontaneous enteritis and increased susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis and commensal and pathogenic pro-inflammatory signals. Subsequent apoptosis of Paneth and goblet cells leads to loss of mucosal barrier function and dysbiosis, further perpetuating inflammation.
