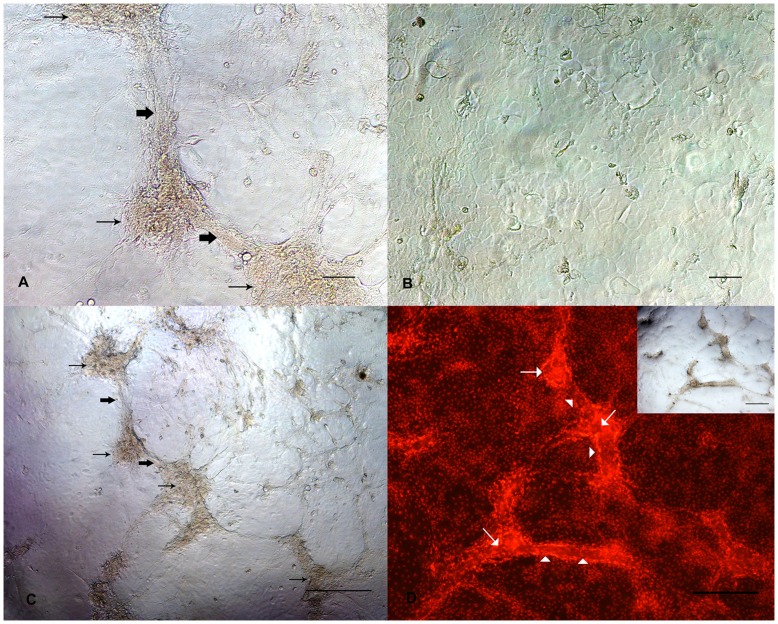
Figure 7. Morphological differentiation of BuMECs cultured in Type I collagen matrix.
A: Phase contrast microscopic image showing development of cellular aggregates (thin arrow) and ‘duct–like’ (bold arrow) structures in BuMECs grown in attached collagen Type I matrix for four days; B: Phase contrast microscopic image of BuMECs grown on plastic substratum for four days shows no such morphological changes; C: Phase contrast microscopic image (low magnification) showing development of cellular aggregates (thin arrow) and ‘duct–like’ (bold arrow) structures in BuMECs grown in attached collagen Type I matrix for four days; D: Fluorescent image of acini-like cellular aggregate and duct- like structure in monolayer of BuMECs grown on attached collagen Type I matrix which is evident from the propidium iodide stained nucleus of the cells forming the structures (insert image show the phase contrast image of the field). Acini-like structure (arrow) constitutes a large aggregate of PI stained nuclei and duct-like structure (arrow head) showing a clear arrangement of PI stained nuclei along the sides of duct-like structure suggesting the formation of wall and lumen. Bars, A and B 100 µm, C and D 500 µm Results represent images from two independent experiments.