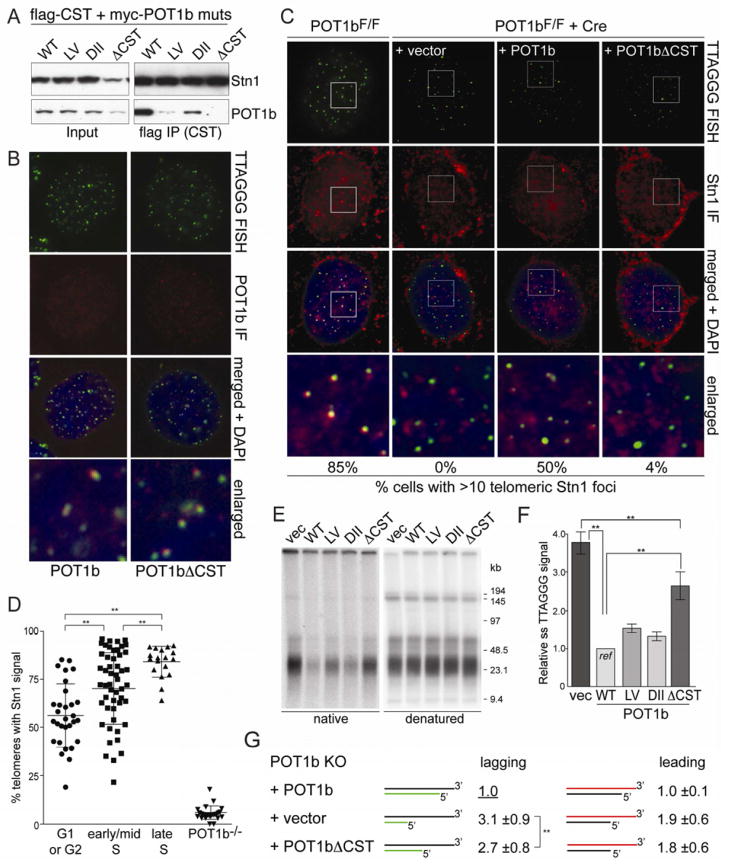
Figure 5. The telomeric function of CST requires its interaction with POT1b.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of POT1b mutants with CST from 293T cells transfected with myc-POT1b alleles and flag-tagged mouse Ctc1, Stn1, and Ten1. FLAG IPs were immunoblotted with FLAG (top) and myc (bottom) Abs. (B) Telomeric localization of POT1b alleles detected by myc IF (red) in POT1bF/− MEFs after deletion of endogenous POT1b with Cre. Telomeres detected by FISH (C-rich probe, green). (C) IF-FISH for co-localization of Stn1 with telomeres in POT1bF/F MEFs (left) and in the same cells expressing the indicated POT1b alleles or vector control, after deletion of endogenous POT1b with Cre. Stn1 (red) was detected with an anti-mStn1 antibody. Telomeres (green) are detected by FISH. Cells with 10 or more mStn1 signals co-localizing with telomeres were scored (bottom) (n>100 nuclei). (D) Quantification of the telomeric localization of Stn1 at different cell cycle phases. Each plotted value represents the percentage of telomeres in an individual cell that contain Stn1 signal detected by IF (n>100 cells). Mean and SDs are shown; ** indicates p<0.05. Cell cycle phases were determined based on BrdU IF pattern. (E, F) Overhang analysis of POT1bF/− MEFs expressing the indicated POT1b alleles at 120 h after Cre. See Fig. 1 for details. (G) Relative overhang size of separated leading- and lagging-end telomeres from POT1bF/− MEFs expressing vector control, wild type POT1b, or POT1bΔCST, after deletion of endogenous POT1b with Cre. Mean values and SDs of 4 independent experiments. See also Fig S6.