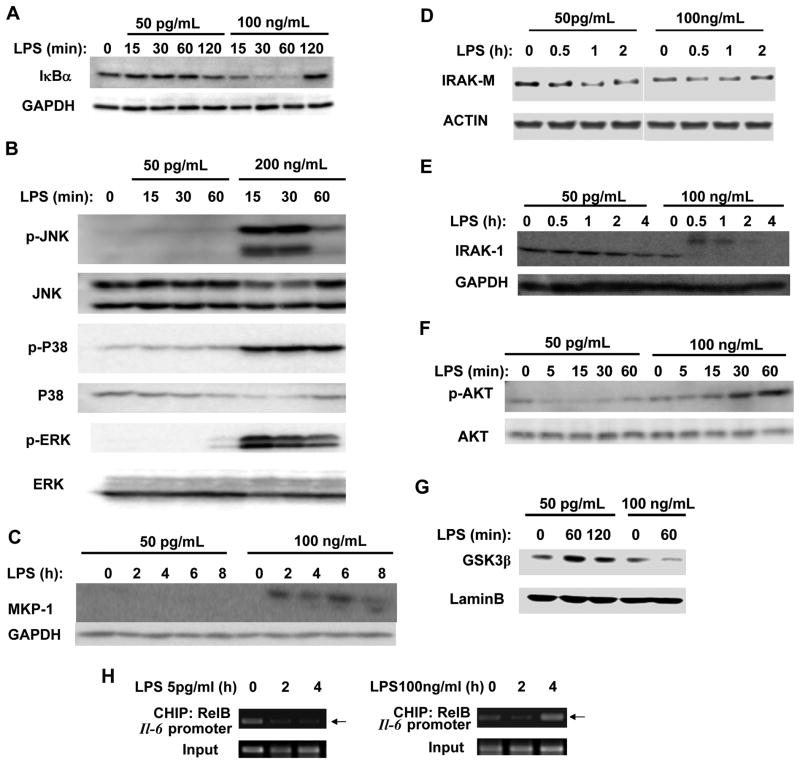
Figure 2. Low dose LPS does not induce the classical NFκB and MAPK pathways, nor negative suppressors for inflammatory responses.
(A) Low dose LPS fails to induce IκBα degradation. WT BMDM were treated with either a low-dose LPS (50 pg/mL) or a high-dose LPS (100 ng/mL) for the indicated times. The levels of IkBα were determined by Western blot. The same blots were probed with Abs specific for GAPDH as loading controls. (B) Low-dose LPS failed to activate the MAP kinase pathways. Whole cell lysates from WT cells treated with either a low (50pg/mL) or high (200ng/mL) dose LPS were harvested and used to determine the levels of phosphorylated JNK, p38 and ERK. The total levels of JNK, p38 and ERK were used as loading controls. (C) Low-dose LPS fails to induce the negative regulators including MKP-1. Total levels of MKP-1 were determined by Western blot. (D) Low dose LPS reduces IRAK-M. Total levels of IRAK-M from cells treated with either a low or high dose LPS were measured by Western blot. (E) Low dose LPS fails to degrade IRAK-1. IRAK-1 levels were determined from cells treated with either low dose or high dose LPS by Western blot. Levels of GAPDH were used as loading controls in Fig C, D, and e. (F) PI3K pathway is activated by high dose LPS, and suppressed by low dose LPS. Whole cell lysates from cells treated with either low or high dose LPS were harvested and used to determine the levels of phosphorylated Akt. The total levels of Akt were used as the loading control. (G) Nuclear GSK3β is induced by low dose LPS, and reduced by high dose LPS. Nuclear lysates from cells treated with low or high dose LPS were harvested and the levels of GSK3β were determined by Western blot. The levels of Lamin B were used as a loading control. Panels were representatives of three independent experiments. (H) CHIP analysis to detect the binding of RelB to the Il-6 promoter in response to high and low dose LPS. WT BMDM cells were treated with either low or high dose LPS for the indicated time periods. The samples were immunoprecipitated using a RelB specific antibody and analyzed by PCR using primers spanning the promoter region of murine Il-6.