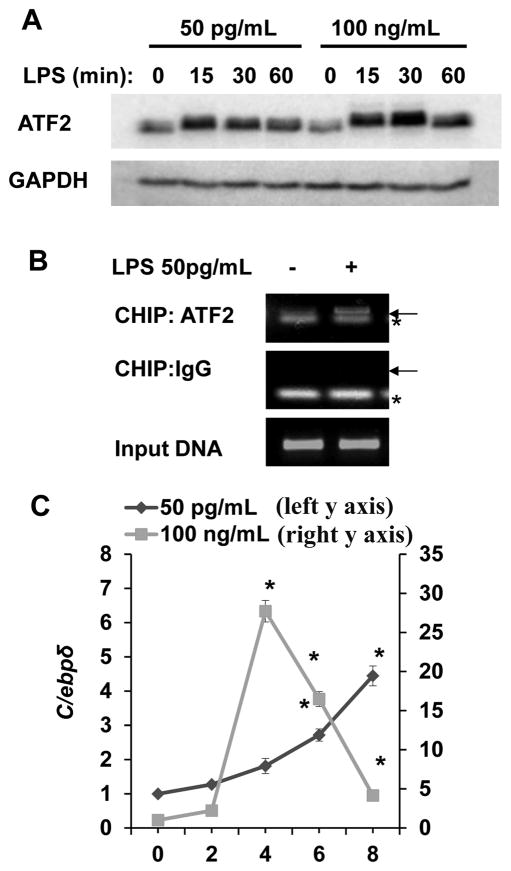
Figure 3. Low dose LPS selectively induces ATF2.
(A) Low-dose LPS induces a rapid increase in ATF-2 protein levels in WT BMDM. WT cells were treated with a low (50 pg/mL) or a high dose (100 ng/mL) LPS for the indicated times. Total ATF2 protein levels were determined by Western blot and GAPDH levels were used as loading controls. (B) Low dose LPS recruits ATF2 to the proximal promoter of the pro-inflammatory gene IL-6 in WT BMDMs. BMDM were either untreated or treated with 50 pg/mL LPS for 2 h and then subjected to ChIP assay using an antibody specific to ATF-2 and primers specific to the proximal promoter of IL-6. The same samples were immunoprecipitated using IgG as a non-specific control and input DNA was analyzed as the loading control. Arrow points to the specific amplification product. * denotes a non-specific band. (C) Low-dose LPS induces a late C/ebpδ expression in WT BMDM. WT cells were treated with either a low (50 pg/mL) or a high dose (100 ng/mL) LPS for the indicated times. C/ebpδ message levels were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. n=3; * p<0.05.