Figure 3.
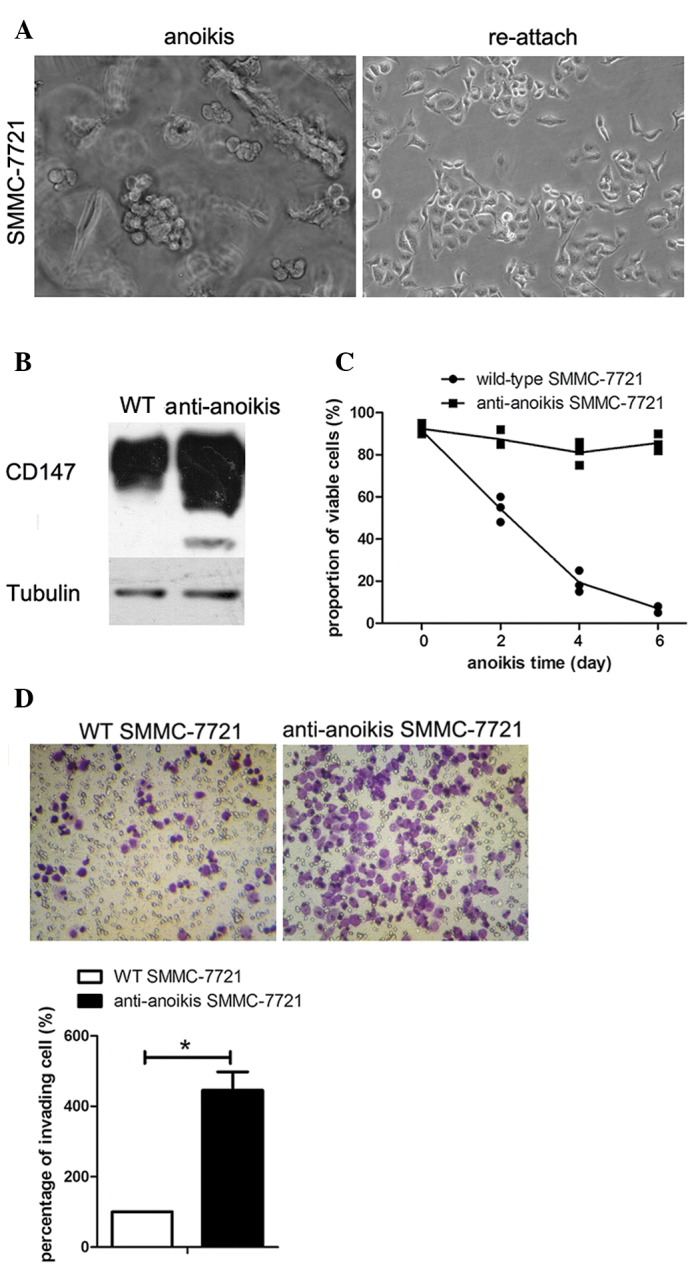
CD147 was significantly upregulated in anoikis-resistant SMMC-7721 cells with an increase in both viability and invasion ability. (A) The process of suspension culture adaptation under a phase-contrast microscope (magnification, ×200). The left panel shows the morphology of SMMC-7721 cells when suspended in methocel medium. The right panel shows the morphology of SMMC-7721 cells following reattachment to the extracellular matrix. The subpopulation of anoikis-resistant SMMC-7721 cells was obtained by sequential cycles of suspension and adhesion culture. (B) Findings of the immunoblot assay with regard to the expression levels of CD147 in wild-type SMMC-7721 cells and the subpopulation of SMMC-7721 cells resistant to anoikis. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) The roportion of viable cells under suspension culture of wild-type SMMC-7721 and SMMC-7721 cells resistant to anoikis at the indicated time-points were detected by trypan blue exclusion assay. Data are the means ± SD for eight replicates. (D) Images of invading SMMC-7721 or anoikis-resistant SMMC-7721 cells in a transwell invasion assay after suspension for 48 h, and column graph for three independent experiments. Data were normalized to wild-type SMMC-7721 cells and are the means ± SD (*p<0.05).
