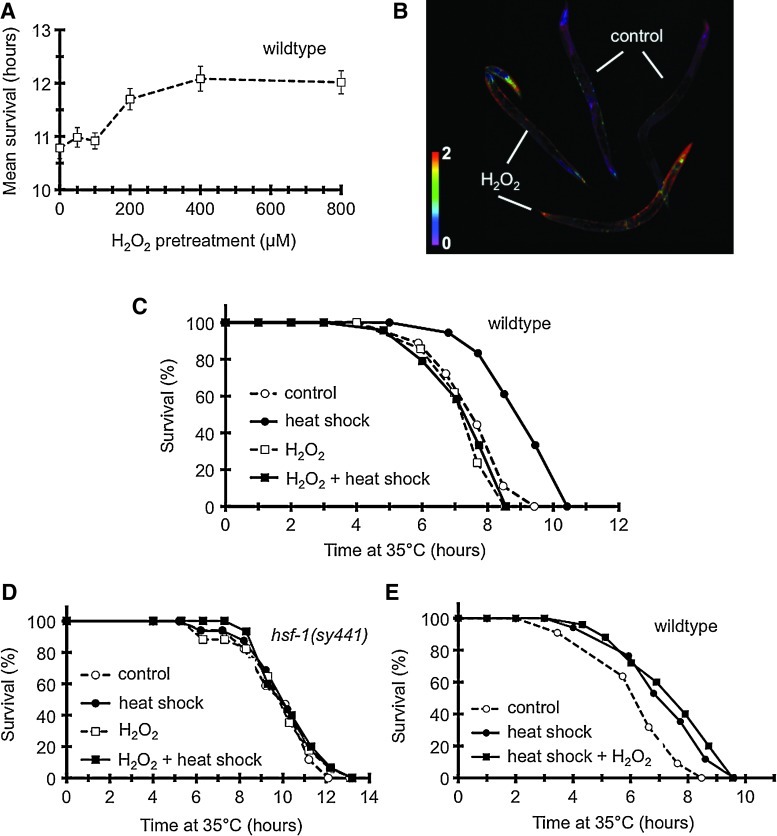
FIG. 4.
A prior H2O2 treatment inhibits aquired thermotolerance in an HSF1-dependent manner in Caenorhabditis elegans. (A) Effect of preconditioning H2O2 treatments on oxidative tolerance. Oxidative stress was applied in the liquid nematode growth medium (NGM) for 1 h at 20°C, 12–14 h before a lethal oxidative challenge. Data are means±SDs of two separate experiments. (B) Intensity-normalized ratio image demonstrating a rapid rise of oxidized/reduced HyPer ratio in jrIs[Prpl-17::HyPer] worms in response to a 1-min challenge by 100 μM H2O2 in liquid NGM. Representative image from five independent experiments. (C) Effect of H2O2 (100 μM for 1 h) on intrinsic and acquired thermotolerance induced by a preconditioning heat shock (heat shock, 30° for 2 h). Lethal heat stress was employed 12 h later. Only heat shock induces a significant difference in survival (p<0.0001). (D) No change in thermotolerance by a preconditioning heat shock and/or an H2O2 treatment in hsf-1(sy441) mutant worms (p>0.1). (E) H2O2 employed after the preconditioning heat shock does not abrogate acquired thermotolerance (p>0.1 compared to heat shock). (To see this illustration in color the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).