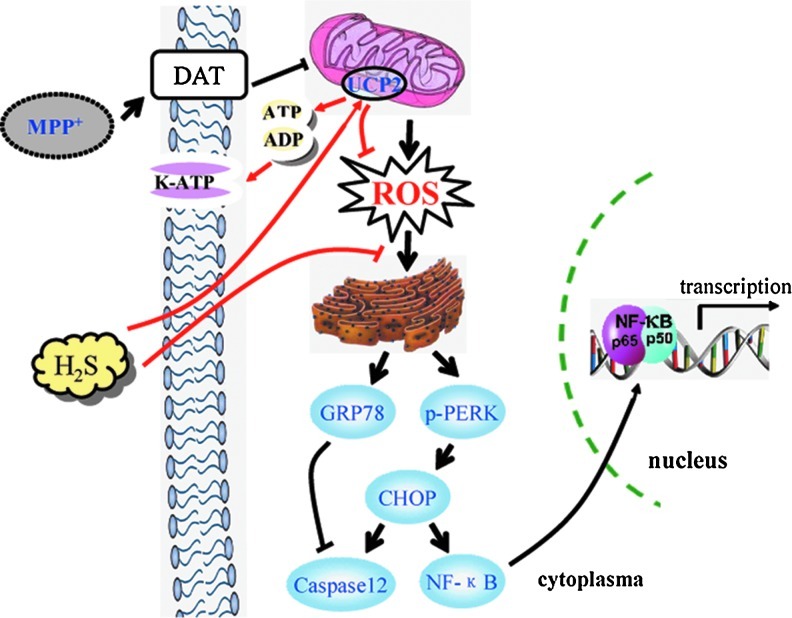
FIG. 8.
Schematic model for the mechanism of H2S in protecting against MPP+-induced neuronal injury. MPP+ is selectively transported into DA neurons by DAT and subsequently inhibits the activity of mitochondrial complex I. Accumulated ROS evokes the upregulation of GRP78 and further triggers ERS. Consequently, p65 nuclear translocation-induced gene transcription or caspase 12-mediated apoptosis occurs in DA neurons. H2S-stimulated mitochondria uncoupling reduces the ratio of ATP/ADP, which in turn opens K-ATP channels. On the other hand, H2S enhances UCP2 function and attenuates ROS production, suppressing ERS and apoptosis induced by MPP+. DAT, dopamine transporter; K-ATP, adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium; H2S, hydrogen sulfide. (To see this illustration in color the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).