FIGURE 1.
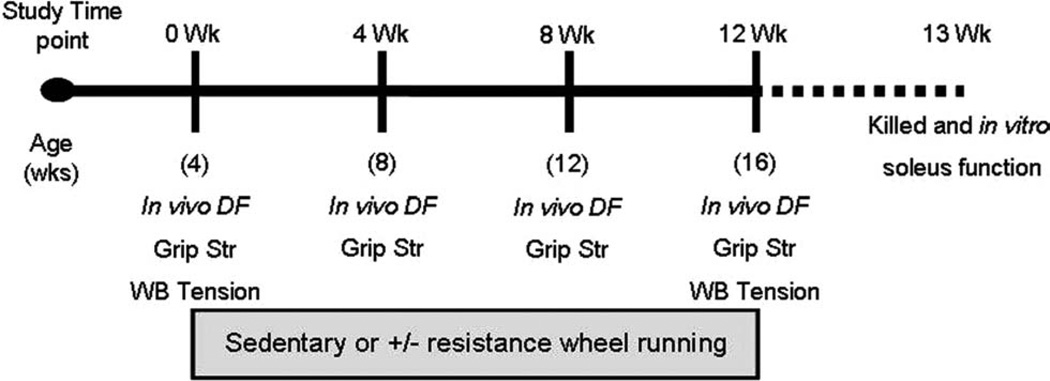
After an initial in vivo strength assessment of dorsiflexion torque (in vivo DF), grip strength (Grip Str), and whole body tension (WB Tension), mice were randomly assigned to either the Sedentary, Free Wheel, or Resist Wheel group (0 Wk). The mice assigned to the Free and Resist Wheel groups initiated running at this time-point. At the 4- and 8-week time-points, all mice were reassessed for in vivo dorsiflexion torque and grip strength. At week 12, all mice were assessed for in vivo dorsiflexion, grip strength, and whole body tension. All mice were killed 1 week later, and skeletal muscles were harvested for in vitro contractility and injury assessment, muscle mass, and Western blot analysis.