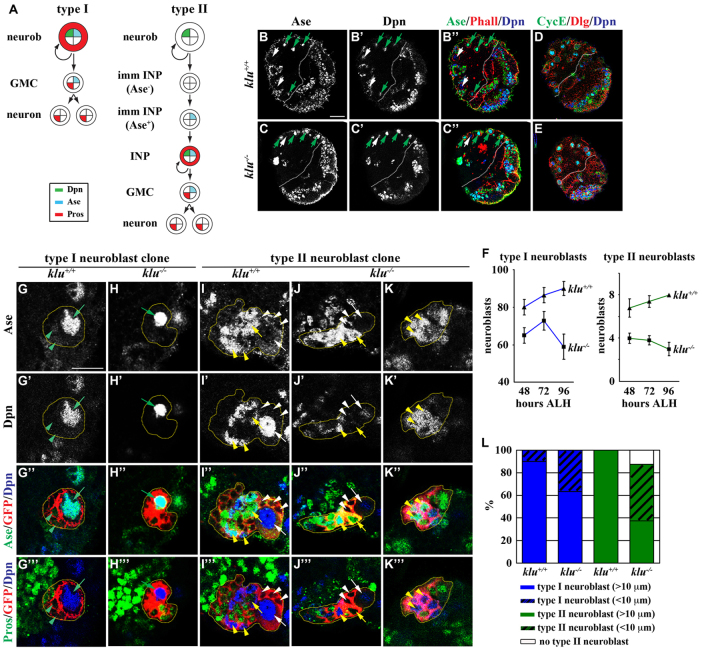
Fig. 1.
Neuroblasts prematurely differentiate in klu mutant brains. (A) Summary of the cell fate marker expression pattern in type I and II neuroblast lineages in Drosophila larval brains. GMC, ganglion mother cell; INP, intermediate neural progenitor; imm INP, immature INP; neurob, neuroblast; Pros, Prospero. (B-F) klu mutant brains show progressive loss of neuroblasts. (B-E) Brains were dissected from wild-type or kluR51/09036 mutant larvae at 96 hours ALH and stained for the markers indicated. The white dotted line separates the central brain (left) from the optic lobe (right). Discs large (Dlg) marks the cell cortex. (F) Average type I and II neuroblasts per brain lobe in larvae of genotypes and stages indicated. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (G-L) Neuroblasts show reduced cell diameter and are likely to prematurely differentiate in klu mutant brains. Larvae carrying GFP-marked klu+/+ or klu−/− mosaic neuroblast clones (outlined by the yellow dotted line) were aged for 110 hours after clone induction and larval brains were stained for the markers indicated. (G-H‴) Type I neuroblast clones. (I-K‴) Type II neuroblast clones. (L) The frequency of klu+/+ or klu−/− clones containing neuroblasts of the cell diameter indicated. The following are indicated: type I neuroblast (Dpn+ Ase+), green arrow; GMC (Dpn− Ase+), green arrowhead; type II neuroblast (Dpn+ Ase−), white arrow; Ase− immature INP (Dpn− Ase−), white arrowhead; Ase+ immature INP (Dpn− Ase+), yellow arrow; INP (Dpn+ Ase+), yellow arrowhead. Scale bars: 20 μm in B-E; 10 μm in G-K‴.