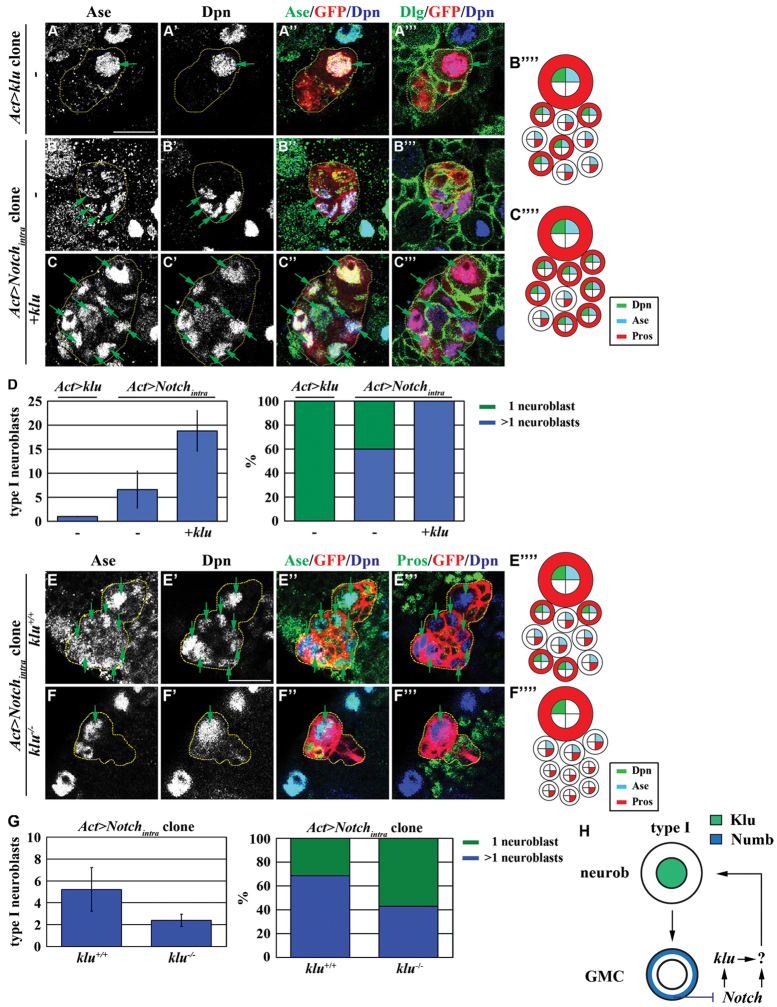
Fig. 7.
Aberrant activation of Notch signaling induces reversion of GMCs in part through klu. (A-D) Co-expression of klu further exacerbates the formation of supernumerary type I neuroblasts induced by constitutively activated Notch signaling. (A-C⁗) Drosophila larvae carrying GFP-marked type I neuroblast lineage clones (outlined by the yellow dotted line) overexpressing klu, Notchintra or klu and Notchintra were aged for 48 hours after clone induction and brains were stained for the markers indicated. (D) Average type I neuroblasts per clone and the frequency of clones containing one or more type I neuroblasts in larvae of the genotype indicated. (E-G) Removal of klu function suppresses supernumerary type I neuroblasts induced by constitutively activated Notch signaling. (E-F⁗) Larvae carrying GFP-marked klu+/+ or klu−/− type I neuroblast mosaic clones (outlined by the yellow dotted line) overexpressing Notchintra were aged for 72 hours after clone induction and brains were stained for the markers indicated. (G) Average type I neuroblasts per clone and the frequency of clones containing one or more type I neuroblasts in larvae of the genotype indicated. (H) Model: Numb prevents the reversion of GMCs to type I neuroblasts by antagonizing Klu. Abbreviations and arrows/arrowheads as Fig. 1. Scale bars: 10 μm.