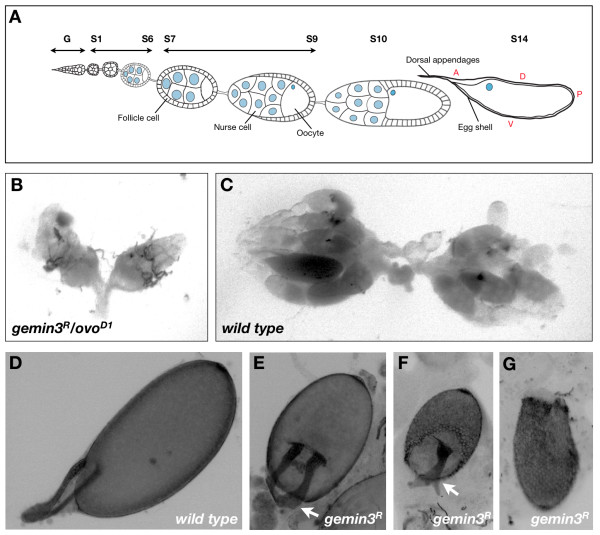
Figure 1.
Ovarian and egg polarity defects in the absence of Gemin3. (A) Schematic of the sequential stages (S1 to S14) of egg chamber development after budding off the germarium (G) [adapted from [30]]. A mature egg (S14) exhibits asymmetry along its A-P and D-V axes. (B, C) Ovaries of gemin3R/ovoD1 female flies are shrivelled in contrast to wild type, a phenotype resulting from the early developmental arrest of gemin3R homozygous germ cells. Images are of the same magnification. (D-G) Compared to wild type, gemin3 mutant eggs are smaller in size and display a range of DA phenotypes including DAs, which are broader and shorter compared to wild type (E, arrow) as well as forked DAs that are fused at their base (F, arrow). Sometimes eggs display a net-like chorion or eggshell with no apparent D-V polarity. In D to G, images are of the same magnification.