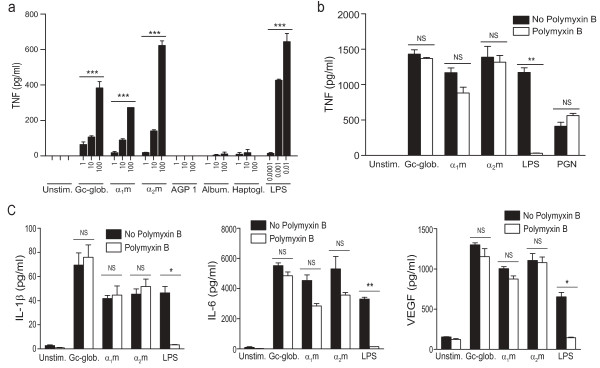
Figure 4.
Plasma proteins detected in osteoarthritic synovial fluid are immunostimulatory. Mouse bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) and human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) were stimulated for 24 hours with plasma proteins detected in osteoarthritic synovial fluid (Table 2), after which cytokine levels in the supernatants were measured with ELISA or Luminex immunoassay. (a) Levels of TNF produced by mouse BMMs stimulated with the indicated concentrations (in μg/ml) of Gc-globulin, α1-microglobulin (α1m), α2-macroglobulin (α2m), α1-acid glycoprotein 1 (AGP 1), albumin, or haptoglobin. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as a positive control. (b) Levels of TNF produced by human MDMs stimulated with 50 μg/ml of α1m, α2m, or Gc-globulin in the presence or absence of 10 μg/ml of polymyxin B, an inhibitor of LPS. LPS (1 ng/ml) was used as a positive control for the efficacy of polymyxin B, and peptidoglycan (PGN; 5 μg/ml), as a negative control. (c) Levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) produced by human MDMs stimulated with 50 μg/ml of Gc-globulin, α1m, or α2m. LPS (1 ng/ml) was used as a positive control. Results are representative of experiments performed at least twice. In (a), data are shown as the mean ± SEM of duplicates. In (b) and (c), data are shown as the mean ± SEM of triplicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant.