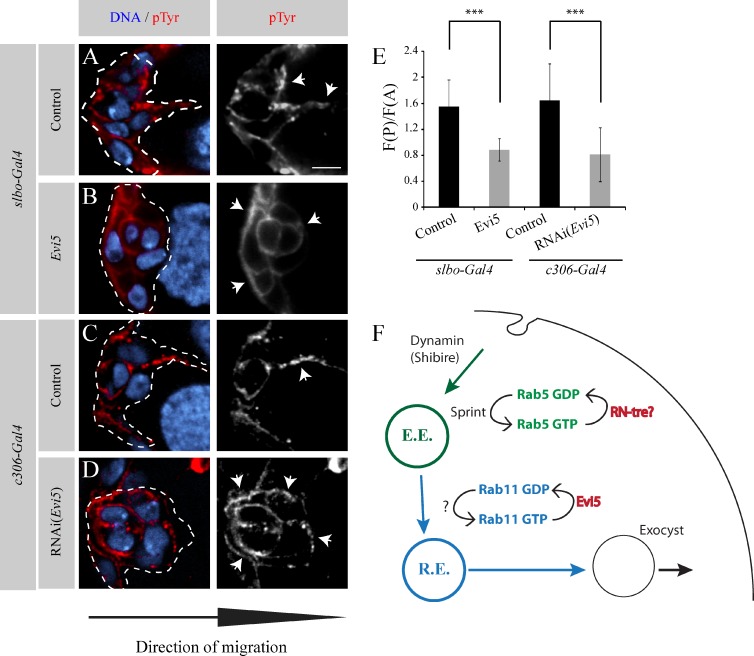
Figure 5.
Evi5 is necessary to properly localize active RTKs at the leading edge of BCs. (A–D) Representative images showing the distribution of pTyr at the onset of the migration process in stage 9 egg chambers in the indicated conditions. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). A grayscale image of the red channel is shown for every image. Dashed lines outline the BC cluster in the colored image. The arrows point to regions with a high pTyr signal. Bar, 5 µm. (E) Quantification of pTyr fluorescence ratio in the posterior half of the cluster (F(P)) to the anterior half (F(A)) at the onset of migration for the indicated conditions. (10 < n < 17; ***, P < 0.005; t test). Error bars are standard deviations. (F) Schematic representation of the endocytic cycle regulating the polarization of RTKs during BC migration. Vesicle trafficking steps illustrated in green and in blue are regulated by Rab5 and Rab11, respectively. Moreover, Evi5, the Rab11-GAP protein identified in this study as a novel regulator of BC migration, is shown in red. RN-tre is shown as the potential Rab5-GAP involved in BC, as it was found in RNAi screen as necessary for BC migration, and its mammalian orthologue is known to act on Rab5. E.E., early endosome; R.E., recycling endosome.