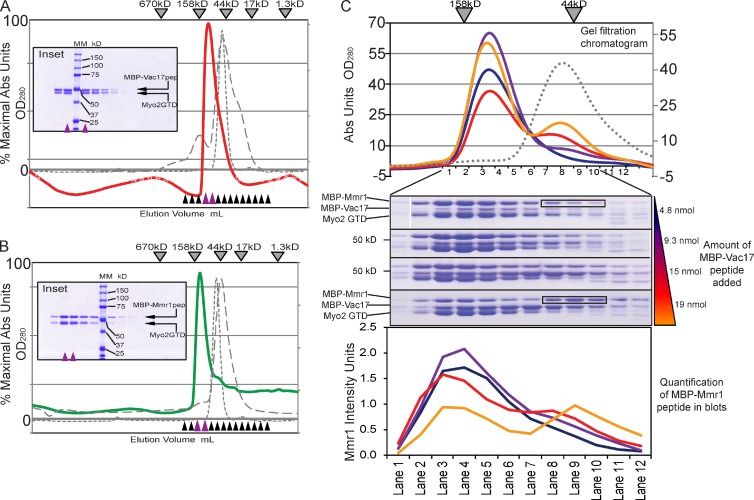
Figure 6.
Vac17 competes with Mmr1 for access to Myo2 in vitro. (A and B) Size-exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200, analytical column). Myo2 CBD and MBP-Vac17(112–157) (1:1 molar ratio; red line); MBP-Mmr1(387–430) (1:1 molar ratio; green line). (inset) Fractions on 10% SDS-PAGE gels. Purple arrowheads show the peak. Black and purple arrowheads show fractions tested on SDS-PAGE. Molecular mass is indicated. Elutions of Myo2 CBD monomer (gray dashed line) and MBP (42 kD) with Myo2 CBD (50.5 kD; gray dotted line). (C) MBP-Mmr1 competes with MBP-Vac17 for binding Myo2 CBD. Equal molar ratios of MBP-Mmr1 peptide (11.7 nmol) and Myo2 CBD (11.4 nmol) were added with increasing amounts of MBP-Vac17; 4.8, 9.3, 15, and 19 nmol (colored wedge) in separate runs. (top) Elutions. Gray dotted line shows MBP-Vac17 plus MBP-Mmr1 (1:1 molar ratio) as a control. (middle) Fractions 1–12 correspond with molecular masses from ∼180 to 30 kD. (bottom) Intensity of MBP-Mmr1 bands. Representative of two independent experiments. Black boxes show fractions on SDS-PAGE that correspond to the MBP-Mmr1 monomer peak of ∼50 kD shown in the chromatogram. Abs, absorbance.