Figure 7.
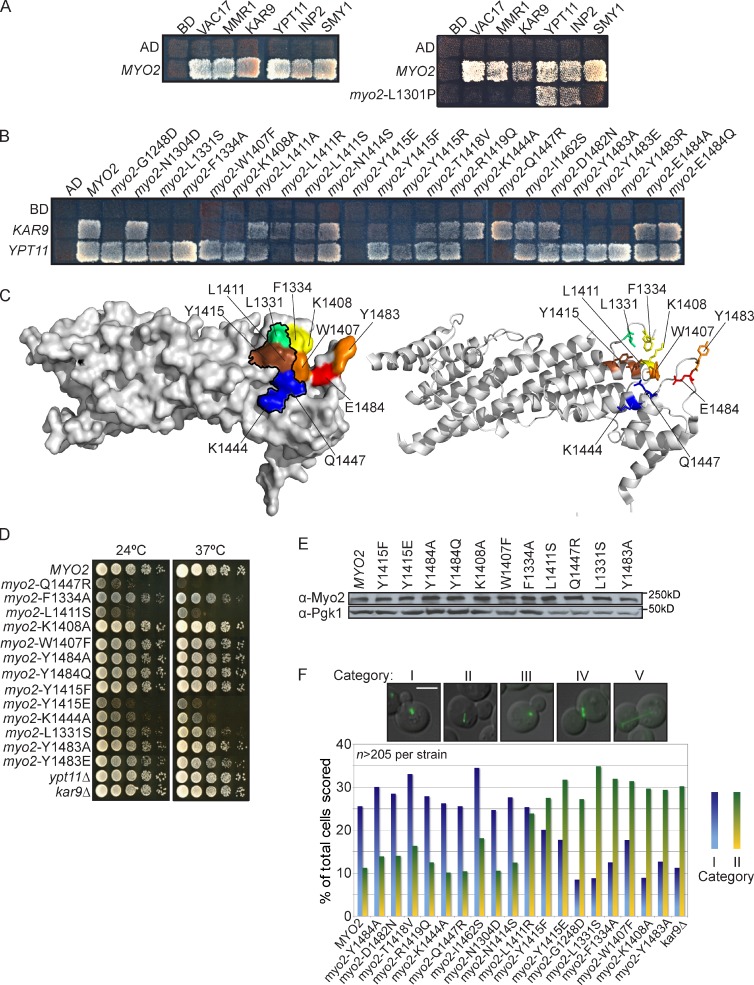
Binding site for the post-Golgi Rab GTPases on Myo2 partially overlaps with the Ypt11, Kar9, and Inp2 binding sites. (A, left) Myo2 CBD interacts with Vac17, Mmr1, Kar9, Ypt11, Inp2, and Smy1 in a yeast two-hybrid test. Effects of L1301P are likely caused by conformational changes in the Myo2 CBD. (right) myo2-L1301P, helix 6, affects binding of Vac17, Mmr1, Kar9, and Smy1. Other mutations in this region do not affect Kar9 and Smy1. (B) Surface residues on Myo2 CBD critical for Kar9 and/or Ypt11 binding. (A and B) Incubated at 24°C for 4 d. Top left squares show empty vector controls. (C) Surface (left) and ribbon (right) view of Myo2 CBD indicating surface residues that interact with Kar9, Inp2, Ypt11, and Ypt31/32. Black outline shows Ypt31/32 and Sec4 binding sites. Red: Inp2 only; orange: Kar9 and Inp2; yellow: Kar9 only; green: Kar9, Sec4, and Ypt31/32; blue: Sec4, Ypt11, and Ypt31/32; brown: Kar9, Inp2, Sec4, Ypt11, and Ypt31/32. (D) Myo2 residues L1331, F1334, W1407, K1408, Y1415, and Y1483, the Kar9 binding site, are critical for orientation of the mitotic spindle. G1248D, an internal residue, also affected spindle orientation. myo2Δ cells with wild-type MYO2 or myo2 mutant plasmids transformed with pGFP-Tub1. Orientation of spindle microtubules scored in five categories: (I) Microtubules aligned toward the bud; (II) microtubules improperly aligned away from the mother–bud neck; categories III, IV, and V (Fig. S3) were not informative. Categories I and II were plotted as a percentage of total cells in all five categories. n = 2; ≥215 cells scored per strain. (E) Steady-state levels of Myo2 unchanged in plasmid-containing strains with myo2 point mutations. (F) Myo2 mutants that affect Kar9 and Inp2 interactions had no effect on growth. Mutations in the Rab GTPase binding site affect growth. Strains were grown to log phase, serially diluted, plated on rich media, incubated at 24°C or 37°C for 2–4 d. Bar, 5 µm. AD, activation domain; BD, binding domain.