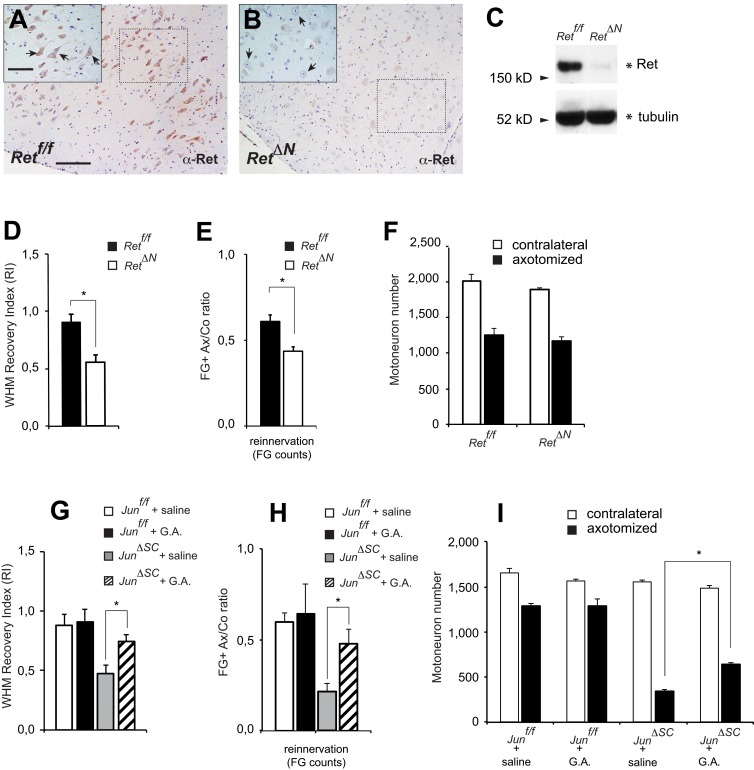
Figure 5.
Ret signaling is involved in the regeneration of facial nucleus motoneurons after axotomy. (A and B) Total Ret IHC in wild-type (A, Retf/f) and mutant (B, RetΔN) healthy animals. Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin & eosin. Facial nucleus (7n) motoneurons express Ret at high levels (A, arrows in inset). The deletion of Ret in these motoneurons by crossing with a Synapsin-Cre deleter mouse was confirmed by the lack of Ret staining in B. Dotted squares indicate the high magnification inset at the top left corner. (C) Facial nuclei from Retf/f and RetΔN mice were microdissected and Ret levels were assessed by Western blot. (D) WHM RI, as in Fig. 1 B, based on Area Under the Curve (AUC) data for each individual animal. RetΔN mice show a significantly poorer response compared with the Retf/f control group (P < 0.01, Student’s t test; n = 6 for each genotype). (E) Target reinnervation of the whisker pad is reduced in RetΔN mice. The graph shows the ratio of retrogradely labeled facial motoneurons on the axotomized (Ax) versus contralateral (Co) side after application of FG to both whisker pads, 28 d after facial nerve cut, followed by 72 h survival; *, P < 0.01, Student’s t test; n = 6 for each genotype; same animals as in D. (F) Motoneuron cell count shows no decrease in survival 31 d after nerve cut in the absence of neuronal Ret when comparing control and mutant animals (n = 6 for each genotype; same animals as in D and E. (G) WHM RI of the four experimental cohorts. Treatment with GDNF and Artemin partially improves functional recovery in the injured JunΔSC mice. *, P < 0.05 in ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey test. In Junf/f mice, treatment with GDNF and Artemin does not have a significant effect over saline (P = 0.49). Group size: n = 10 Junf/f + saline, n = 2 Junf/f + G.A., n = 5 JunΔSC + saline, and n = 8 JunΔSC + G.A. mice. (H) Treatment with GDNF and Artemin also significantly improves target reinnervation (whisker pad) in JunΔSC mice. The graph shows the axotomized versus contralateral ratio for FG-labeled facial motoneurons using the same animals as in G. As in G, the neurotrophin treatment did not significantly improve target reinnervation in Junf/f mice (P = 0.78 in post-hoc Tukey test). (I) Total motoneuron cell count showing a significant but partial rescue of motoneuron survival just in the JunΔSC mice 31 d after nerve cut. Group size in G–I: n = 6 Junf/f + saline, n = 3 Junf/f + G.A., n = 5 JunΔSC + saline, and n = 8 JunΔSC + G.A. mice. Bars: (A; also applies to B) low magnification, 200 µm; high magnification insets, 100 µm.