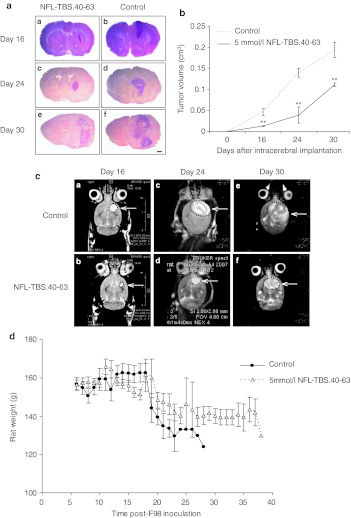
Figure 5.
Intracerebral administration of the NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide reduces tumor growth. (a) Typical coronal sections of brains stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H/E) from rats treated with the NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide (A, C, E) or saline (B, D, F). Brains were recovered at 16 (A, B), 24 (C, D), and 30 days (E, F) following glioma cell transplantation. Black bars, 1 mm. (b) Tumor volumes in NFL-TBS.40-63-treated and control animals (mean ± SEM of three animals per treatment group at each post-transplant age). Tumor volume was determined by histomorphometry on serial sections. Compared to controls, tumor volume in rats treated with the NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide is reduced by 72% at 16 and 24 days post-transplantation, and by 42.8% at 30 days post-transplantation. Asterisks indicate significant level versus control **P < 0.005. (c): T2-weighted axial magnetic resonance images of rat brains treated with NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide (A, C, E) or vehicle (B, D, F), at days 16, 24, or 30. MRI evaluation revealed a similar reduction in tumor volume following NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide treatment. (d) Mean weights of glioma-bearing animals following peptide or vehicle treatment. MRI, magnetic resonance imagery; NFL, neurofilament light; TBS, tubulin-binding site.