Fig 2.
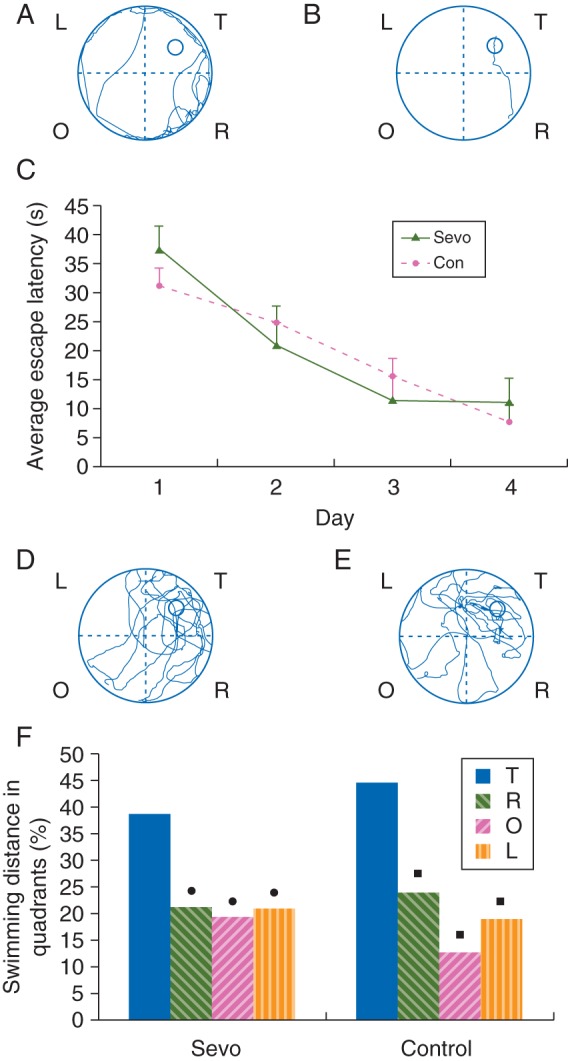
Effects of sevoflurane exposure at P7 on spatial learning and memory abilities of P28–32 rats in the MWM test. The learning and memory abilities of sevoflurane- (n=9) and air-treated (control, n=9) rats were assessed using place navigation (a–c) and spatial probe trials (d–f). A representative route of a control rat to reach the escape platform on day 1 (a) and day 4 (b). (c) The latencies to reach the escape platform in the 4 day place navigation trials, which show no significant differences between the control and sevoflurane groups. The results are expressed as the mean (sem) time in seconds. (d and e) A representative route of a sevoflurane-treated rat (d) and a control rat (e) in search of the escape platform on day 5. T, target quadrant; R, O, L, quadrants which were to the right, opposite, or left of the target quadrant. (f) A comparison of the average percentage of the swimming distance in each quadrant of the MWM for the sevoflurane and control groups. The target quadrant (T) in the spatial probe trial demonstrates the retention ability of spatial learning and memory in MWM. •P<0.05 compared with the T quadrant within the sevoflurane group; ▪P<0.05 compared with the T quadrant within the control group. There were no significant differences between the control and sevoflurane groups in any of the quadrants of the MWM.
