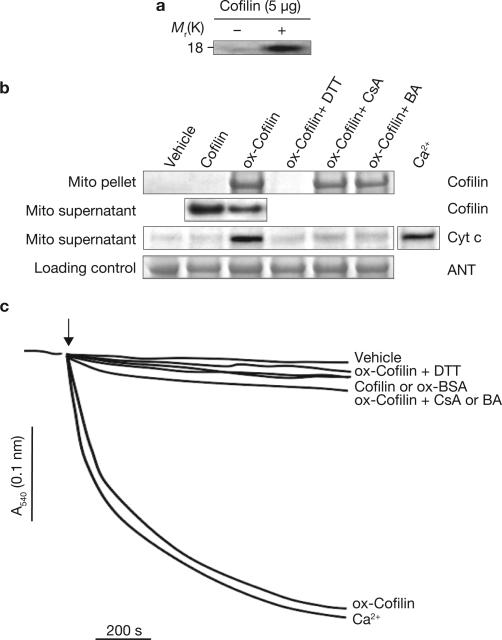
Figure 2.
Oxidized cofilin binds to mitochondria, causing their swelling and cytochrome c release through opening of the PTP. (a) Recombinant human cofilin was oxidized by TnCl in vitro as described in the Methods. The figure shows detection of cofilin disulphides by 5-IAF-labelling and SDS–PAGE (fluorescein fluorescent band). (b) Rat liver mitochondria were exposed to purified, recombinant cofilin (5 μg for 10 min at 37 °C) that was either untreated or previously oxidized (ox-cofilin) with TnCl (100 μM). Mitochondria were treated in the presence or absence of the mitochondrial PTP inhibitors cyclosporine A (CsA; 2 μM) or bongkrekic acid (BA; 50 μM). A sample of ox-cofilin was treated with the sulphydryl reducing agent DTT and then dialysed before adding to the mitochondria to assess the role of cofilin disulphide bonds on its biological activity. The vehicle control contained TnCl (2 μM), which has no direct effect on the mitochondria6. Cofilin protein in the mitochondrial (Mito) pellet and cytochrome c in the supernatant were assessed by a western blot immunoassay (30 μg protein per lane). Adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) was used as a loading control for the mitochondrial pellet fraction. The remaining unbound cofilin and the cytochrome c (Cyt c) released by Ca2+ treatment (150 μM CaCl2) were assessed in the mitochondrial supernatants. (c) Swelling of mitochondria exposed to native or oxidized cofilin, or oxidized bovine serum albumin (ox-BSA; 5 μg) was measured as described in the Methods. Ca2+ (150 μM CaCl2) was used as a positive control for induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition. DTT and CsA or BA treatments were as described in b. Control (vehicle) mitochondria were stable and showed no swelling under the same incubation conditions. The data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.