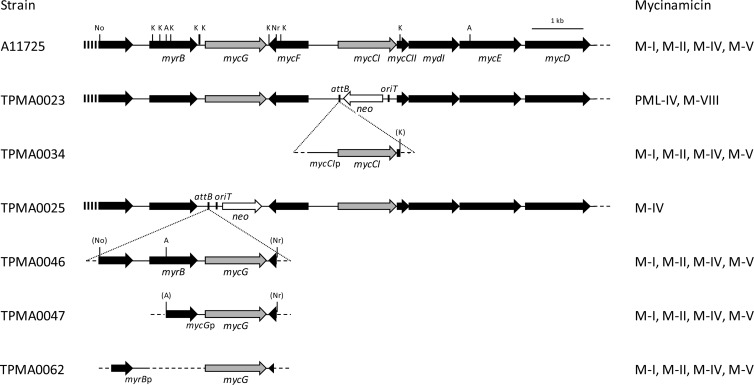
Fig 2.
Physical maps of the region, including mycCI, mycG, and the flanking genes of the wild strain Micromonospora griseorubida A11725, mycCI disruption mutant TPMA0023, and mycG disruption mutant TPMA0025 and the DNA fragments introduced into these disruption mutants for the gene complementation study. The major mycinamicins in the culture broth of the wild strain, disruption mutants, and respective complementation strains (TPMA0034, mycCI; TPMA0046, TPMA0047, and TPMA0062, mycG) were detected with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (see Fig. S2 and S4 in the supplemental material). The relevant restriction sites are indicated as follows: A, ApaLI; K, KasI; No, NotI; and Nr, NruI. Mycinamicins in the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extracts from the culture broth were analyzed with HPLC. Trace amounts of M-IV and M-V were detected in strains A11725, TPMA0034, TPMA0046, TPMA0047, and TPMA0062.