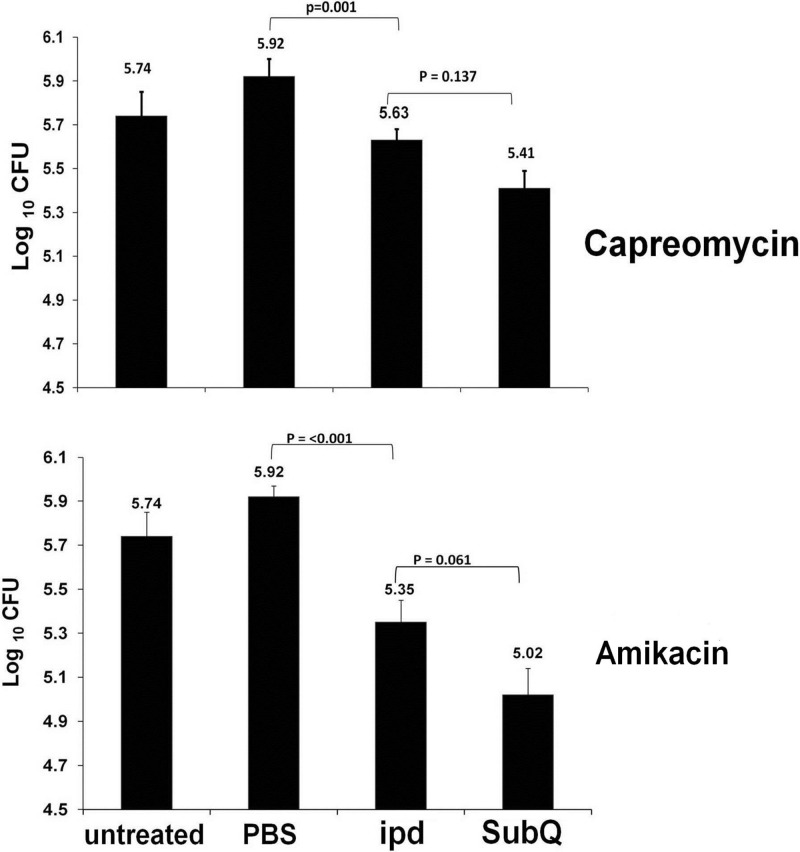
Fig 2.
Bacterial loads in the lungs of M. tuberculosis-infected mice after capreomycin or amikacin intrapulmonary aerosol delivery or subcutaneous injection. Groups of mice (n = 6) were treated with amikacin or capreomycin by subcutaneous injection (subQ) at 3,300 μg/dose five times a week or aerosol intrapulmonary delivery (ipd) at 500 μg/dose three times a week. Other groups of M. tuberculosis-infected mice were used as controls (untreated) or treated by aerosol intrapulmonary delivery with 50 μl/dose three times a week of the PBS used as a drug diluent (PBS).