Fig 2.
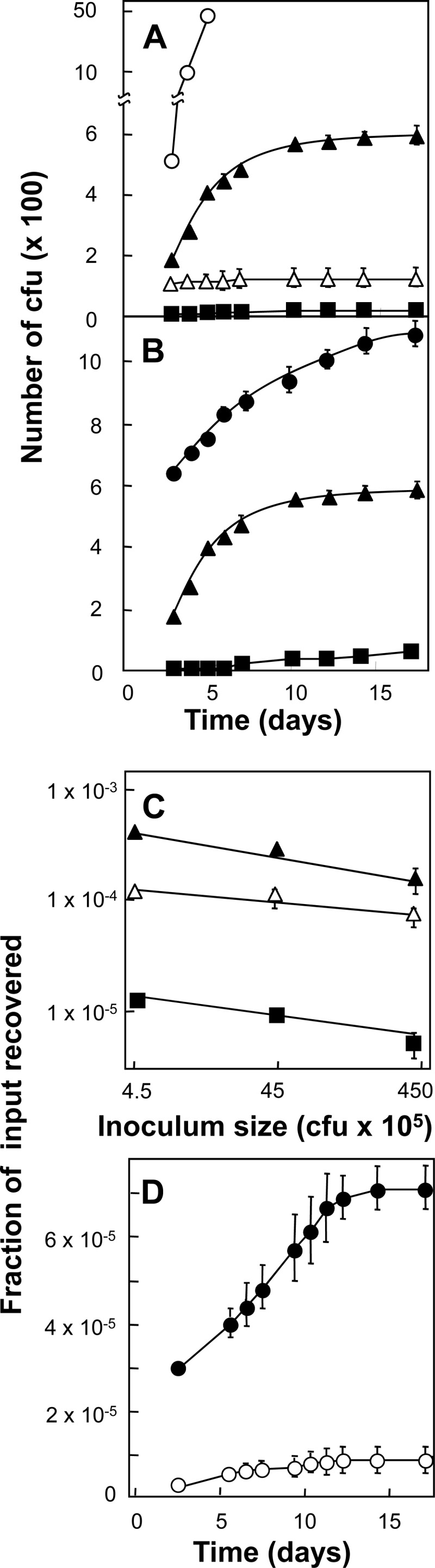
Ciprofloxacin-resistant mutants of M. smegmatis induced by ciprofloxacin. Exponentially growing cultures of M. smegmatis strain KD1163 were applied to ciprofloxacin-containing agar and incubated at 37°C, and at daily intervals, the cumulative number of colonies was determined. (A) Effect of ciprofloxacin concentration. An inoculum of 4.5 × 106 CFU was applied to agar containing various concentrations of ciprofloxacin (MIC = 0.2 μg/ml). Symbols: empty circles, 0.4 μg/ml; filled triangles, 0.8 μg/ml; empty triangles, 1.6 μg/ml; filled squares, 3.2 μg/ml. (B) Effect of inoculum size. Various numbers of cells were applied to agar containing 0.8 μg/ml ciprofloxacin (4 times the MIC). Symbols: filled circles, 4.5 × 107 CFU; filled triangles, 4.5 × 106 CFU; filled squares, 4.5 × 105 CFU. (C) Effect of inoculum size on fractional recovery of mutants. Data such as those shown in panel B were used to determine the number of colonies measured at several concentrations of ciprofloxacin on day 10, corrected for pre-existing mutants by subtraction of the number of colonies found on day 3. Symbols: filled triangles, 0.8 μg/ml (4 times the MIC); empty triangles, 1.6 μg/ml (8 times the MIC); filled squares, 3.2 μg/ml (16 times the MIC). (D) Effect of a recA deficiency on mutant induction. Wild-type strain mc2155 (KD2045; filled circles, MIC = 0.5 μg/ml) and recA-deficient strain HS42 (KD2046; empty circles, MIC = 0.2 μg/ml) were applied to agar containing ciprofloxacin at 2.5 times the MIC, and at the indicated incubation times, colony numbers were determined and plotted as a fraction of the number of CFU applied to the plates. Error bars for panels A, B, and D represent standard deviations; similar results were obtained with two replicate experiments.
