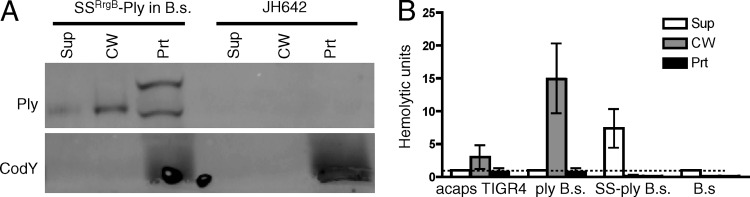
Fig 3.
SSRrgB-Ply expression in Bacillus subtilis. (A) SSRrgB-Ply can be secreted when expressed in B. subtilis. SSRrgB-Ply was placed under the control of the Pspac* promoter in the amyE locus on the B. subtilis chromosome. All strains were grown to mid-exponential phase, fractionated into supernatant, cell wall, and protoplast compartments, and assayed for the presence of Ply and CodY by Western blotting. SSRrgB-Ply in B.s., SSRrgB-Ply fusion in B. subtilis; JH642, wild-type B. subtilis parent strain. Equal cell equivalents were loaded on the gel. Sup, culture supernatant; CW, cell wall; Prt, protoplast. (B) Hemolytic assay of culture supernatant, cell wall, and protoplast fractions of acapsular S. pneumoniae (acaps TIGR4), B. subtilis with ply (ply B.s.), B. subtilis with SS-ply (SS-ply B.s.), and B. subtilis parent strain JH642 (B.s). The ply in B. subtilis has the same distribution as in S. pneumoniae, with the highest hemolytic activity in the cell wall fraction. The supernatant fraction has the highest hemolytic activity in the SS-ply B. subtilis strain. No hemolytic activity was detected in the B. subtilis parent strain. The dotted line indicates the limit of detection. Bars show the means for three biological replicates; error bars indicate standard errors of the means (SEM).