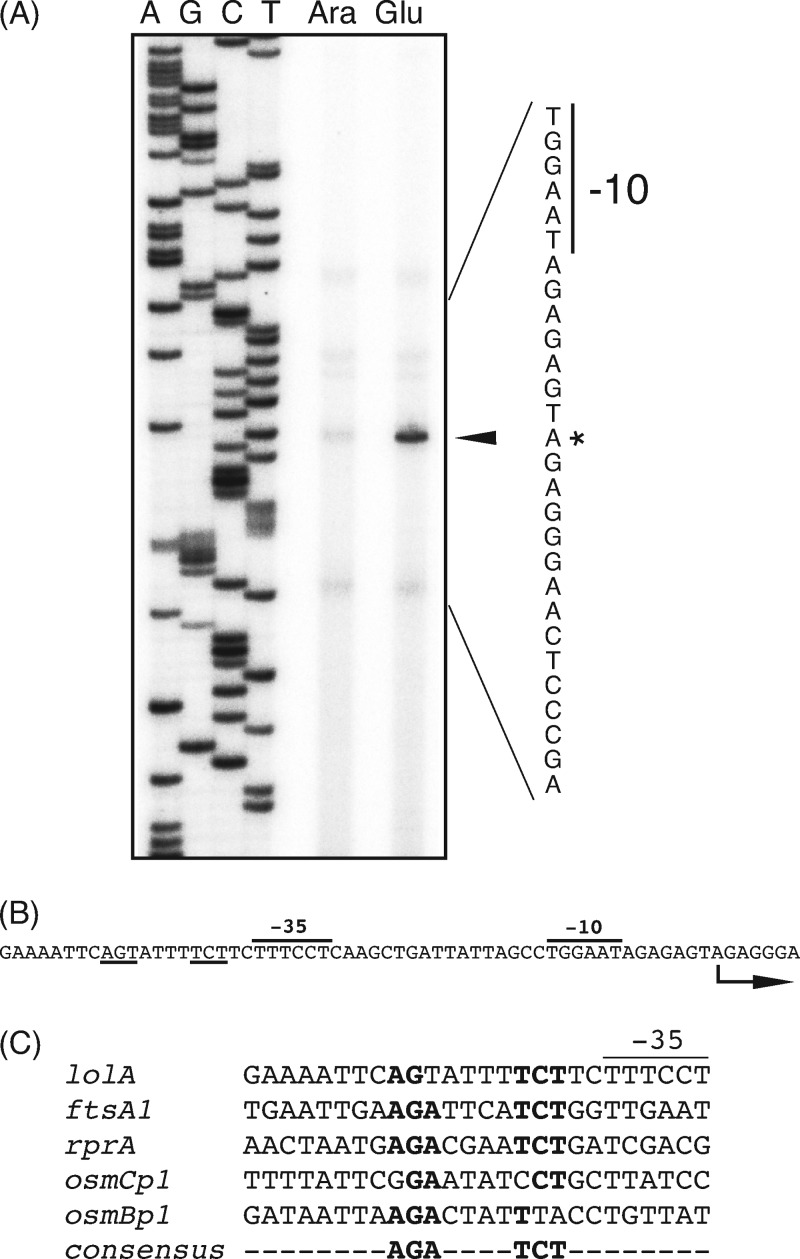
Fig 6.
Identification of the lolA promoter and the RcsB-binding motif. (A) Primer extension analysis of the lolA transcript. Total RNA was isolated from cells grown as described in the legend of Fig. 2B. The 32P-labeled lolA-specific oligonucleotide primer was hybridized to RNA isolated from LolB-expressing (lane Ara) or LolB-lacking (lane Glu) cells and extended by reverse transcriptase. Extension products were analyzed on a 6% polyacrylamide gel containing 8 M urea. Sequencing reaction products (lanes A, G, C, and T) of the lolA promoter region with the same primer were electrophoresed alongside. The arrowhead indicates the extension product specific for lolA. The nucleotide sequence of the corresponding region is shown on the right. The asterisk indicates the transcription start site. (B) Nucleotide sequence of the lolA promoter region. The promoter −35 and −10 sequences are indicated, and the RcsB-binding consensus sequences are underlined. The arrow indicates the transcription start site. (C) Sequence similarities among RcsA-independent promoters. The nucleotide sequences around the proposed RcsB-binding sites are shown. The consensus sequence for the RcsB recognition site is also shown at the bottom.