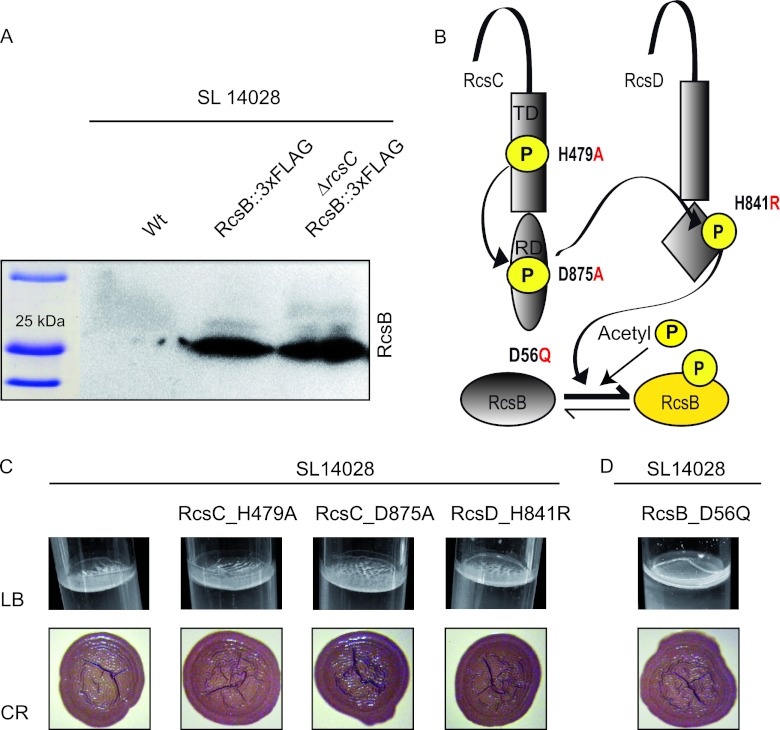
Fig 2.
Change of phosphorylatable residues in the Rcs pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of RcsB expression in S. Typhimurium wild-type strain 14028 and the 14028 ΔrcsC mutant. Samples for protein analysis were taken after 72 h of incubation under LB medium biofilm-forming conditions. (B) Schematic diagram showing the Rcs transduction signal. The residues involved in phosphate transfer from the RcsC kinase via RcsD to the response regulator RcsB and the changes undertaken are indicated. The possibility of RcsB phosphorylation via acetyl phosphate is also shown. P, phosphoryl group; RD, receptor domain; TD, transmitter domain. (C) Biofilm phenotypes. Shown is the pellicle formation capacity in LB medium at room temperature and colony morphology on Congo red agar plates of S. Typhimurium wild-type strain 14028 and the 14028 RcsC_H479A, 14028 RcsC_D875A, and 14028 RcsD_H841R strains. (D) Pellicle formation capacity in LB medium at room temperature and colony morphology on Congo red agar plates of the S. Typhimurium 14028 RcsB_D56Q strain.