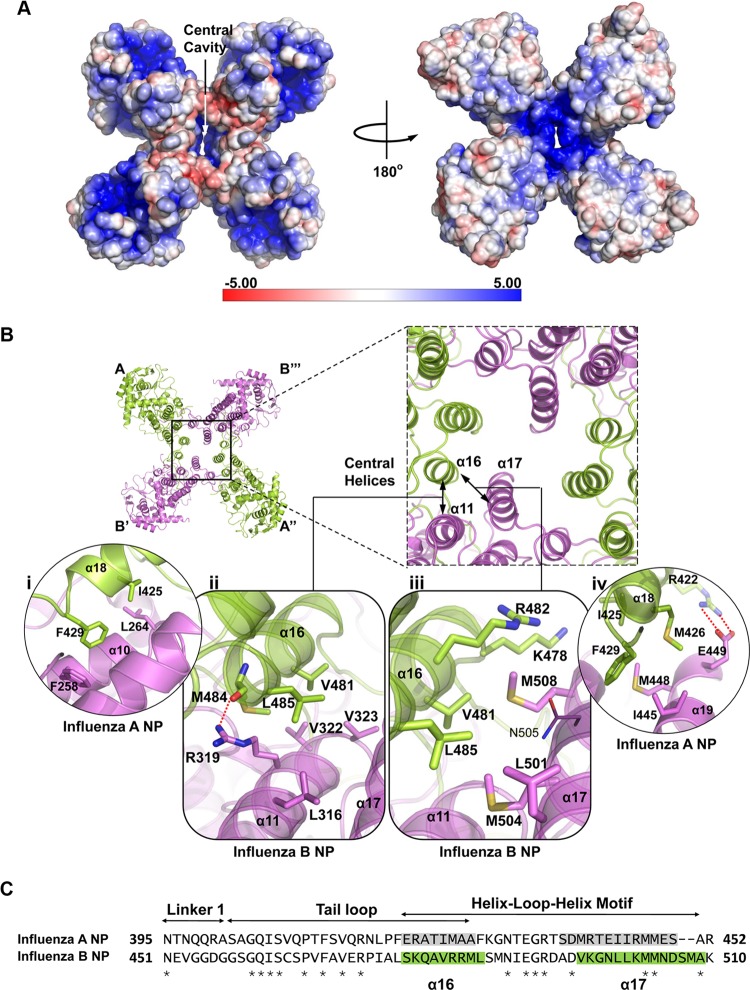
Fig 5.
Tetramer formation of BNP. (A) Electrostatic potential representation of BNP tetramer. The RNA-binding groove is located at the periphery of the tetramer, at the highly positively charged region. An obvious space is observed in the middle of the tetramer. (B) Interactions of the central helices of ANP and BNP. (i) Hydrophobic interactions between α10 and α18 in ANP. (ii) In BNP, M484 of the tail loop forms electrostatic interactions with R319 of the neighboring BNP molecule. V481 of the tail loop also forms hydrophobic interactions with V322 and V323 of the neighboring BNP. M484 and L485 form another van der Waals contacts with R319. (iii) K478 and N505 do not form salt bridges in BNP. Instead, M508, which is not found in ANP, interacts with K478, V481, and R482. (iv) The R422-E449 salt bridge is prominent in ANP. (C) Sequence alignment of influenza A and B shows that the regions for homo-oligomerization are less conserved (29% identical). Shaded regions are the helices α16 and α17 of the helix-loop-helix motif. α17 is especially misaligned between the two NPs and suggests that the motif is flexible in nature. Stars indicate identical sites.