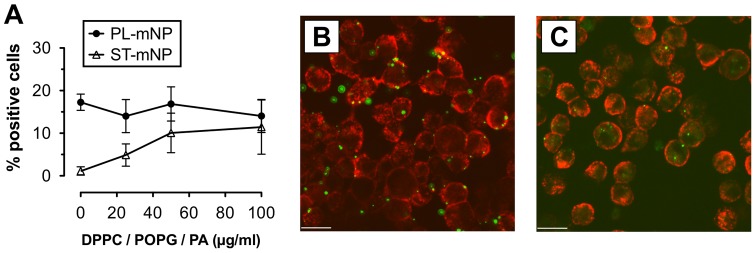
Figure 5. Effect of surfactant lipids on the association of nanoparticles with alveolar macrophages.
(A) Starch- (ST) or Phosphatidylcholine-modified (PL) magnetite nanoparticles (mNP; 1.532×1010/ml) were incubated with alveolar macrophages (AM; MH-S cells) for 90 min in the absence or presence of 25, 50 or 100 µg/ml (total lipids) of surfactant-like membrane vesicles composed of dipalmitoyl-glycero-phosphocholine (DPPC), palmitoyl-oleoyl-glycero-phosphoglycerol (POPG) and palmitic acid (PA). Cells with Fl-1>101 were considered as positive cells for nanoparticle association and uptake (plotted as percent of positive cells with respect to total cells) compared to control (cells only). Data shown as mean ± SD (n = 6). Images are representative micrographs of AM (membrane in red) with ST-mNPs (B) or PL-mNPs (C) (in green), both in the presence of 100 µg/ml DPPC/POPG/PA. Scale bar indicates a distance of 20 µm.