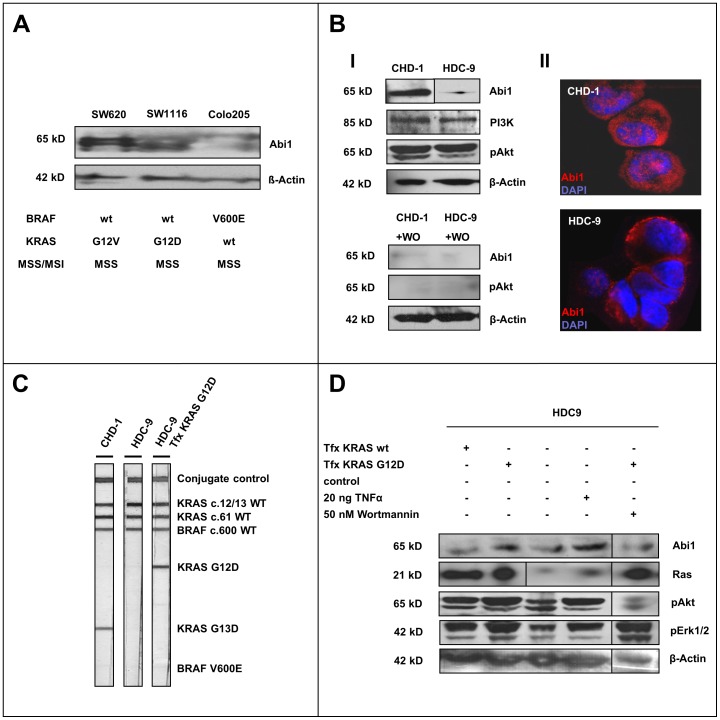
Figure 3. Abi1 in colorectal cancer cell lines. A.
, Abi1 immunoblotting of colorectal carcinoma whole cell line lysates with different KRAS/BRAF mutation status shows upregulation of Abi1 in KRAS-mutated SW620 and SW1116, but only a faint signal in BRAF-mutated Colo205 cells. B, Immunoblotting of CHD-1 and HDC-9 cell lysates show overexpression of Abi1 in CHD1 cells, while both cell lines express comparable amounts of PI3K (I). There is slightly stronger Akt phosphorylation in CHD1 compared to HDC9 cells. Application of 50 nM Wortmannin (WO) almost completely repressed the pAkt and Abi1 signals. Immunofluorescence microscopy shows strong cytoplasmatic and nuclear Abi1 staining in CHD-1 cells, but only a faint cytoplasmatic signal in HDC-9 cells (II). C, KRAS/BRAF mutation testing reveals an activating KRAS G13D mutation in CHD-1 (left lane), while HDC-9 cells are KRAS wild-type (central lane). Transfection of HDC-9 cells with a KRAS G12D-construct leads to appearance of a band indicating a KRAS G12D-mutation (right lane). Both cell lines are BRAF wild-type. D, Immunoblotting of HDC-9 after transfection, TNFalpha and Wortmannin treatment shows an increase in pErk1/2 and pAkt and overexpression of Abi1 upon transfection with constitutively active KRAS G12D (2nd lane) compared to both control (3rd lane) and to transfection with wild-type KRAS (1st lane). Stimulation with TNFalpha also enhances phosphorylation of signaling proteins and leads to upregulation of Abi1 (4th lane). The overexpression of Abi1 could be reversed by application of 50 nM Wortmannin (5th lane).