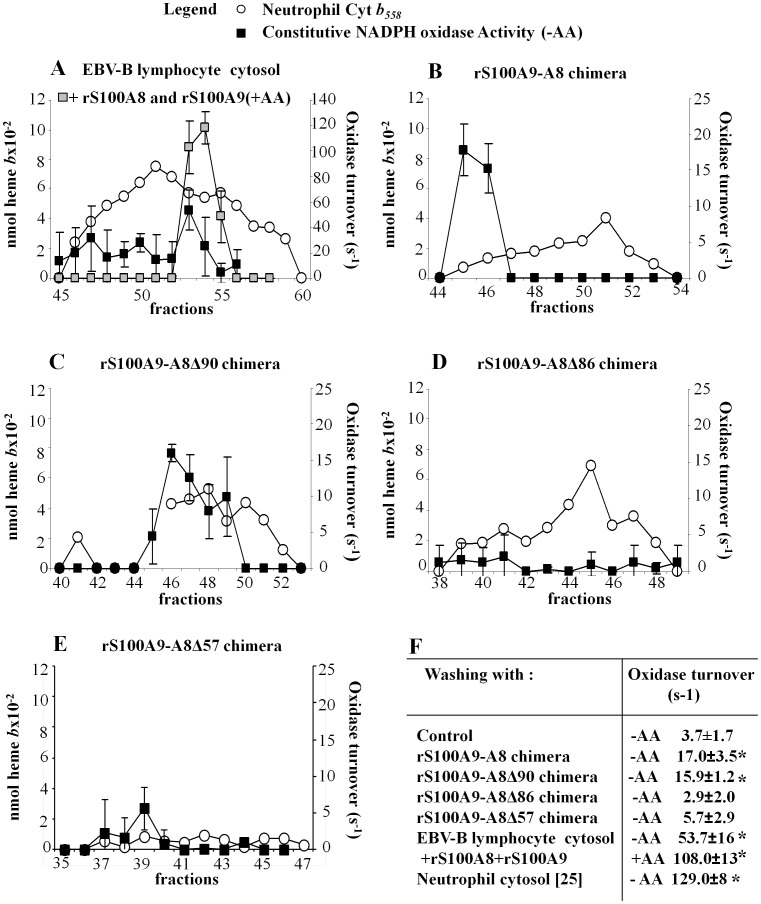
Figure 6. Constitutive NADPH oxidase turnover of the purified cytochrome b558 isolated from stimulated neutrophils on heparin affinity matrix in the presence of rS100A9-A8 full length or truncated chimeras.
Purification of cytochrome b558 from stimulated neutrophils followed a standard protocol until it bound to the heparin affinity matrix as reported [25] and as described in Materials and Methods. The cytochrome b558 bound to the affinity heparin matrix was washed with: (A) EBV-B lymphocyte cytosol; in some experiments, a 1/1 mixture of rS100A8 and rS100A9 was added to the Sephacryl eluted cytochrome b558 and then the activity of NADPH oxidase was measured in the presence of (1 mM) arachidonic acid (grey square). (B) S100A9-A8; (C) S100A9-A8Δ90; (D) S100A9-A8Δ86; (E) S100A9-A8Δ57. S100 chimera proteins were preloaded with calcium (500 nM). After the washing step, eluted fractions containing cytochrome b558 were pooled and filtrated on Sephacryl-S300. The concentration of cytochrome b558 in the Sephacryl eluted fractions (open circle) was determined by measuring the “reduced minus oxidized” differential spectrum at 426 nm. NADPH oxidase activity of purified cytochrome b558 was measured in a cell free assay with 0.2 pmol cytochrome b 558/assay, in the presence of 10 µM FAD, 40 µM GTPγS, and 5 mM MgCl2 but without arachidonic acid, and after adding 150 µM NADPH. The NADPH oxidase activity was expressed as turnover (s−1) (black squares). No S100A9-A8 chimera or EBV-B lymphocyte cytosol was added to the heparin matrix, in control experiments. (F) Table representing the optimum NADPH oxidase turnovers obtained in A, B, C, D, E conditions, or by using cytosol of stimulated neutrophils instead of that of EBV-B lymphocytes [25]. Number of experiments n = 6 *p<0.05 compared to control (constitutive NADPH oxidase activity of purified cytochrome b558 in control experiment).